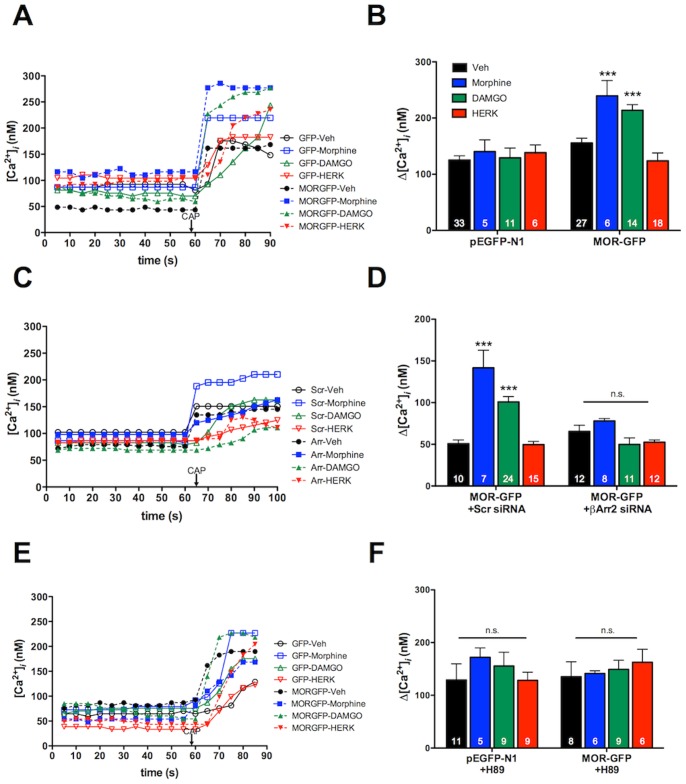
Figure 3. Pretreatment with morphine or DAMGO increases capsaicin responses in primary sensory neurons, and requires β-arrestin2 and PKA activation.
A, B) TG neurons from rats were nucleofected with MOPr-GFP or empty vector (GFP), and treated with morphine (1 μM), DAMGO (1 μM), herkinorin (10 μM), or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for 15 min. Real-time calcium responses from individual GFP-positive cells were measured before and after exposure to capsaicin (CAP, 50 nM) and the net change in intracellular calcium accumulation (Δ[Ca2+]i) was determined. Representative traces (A) and the mean ± SEM (B) of the difference in pre- and post-capsaicin (CAP) response for the number of cells indicated at the bottom of each bar (B). *,** p<0.05, 0.01 by two-way ANOVA. C, D) TG neurons from rats were nucleofected with MOPr-GFP. 24 h later, cells were transfected with siRNA targeting β-arrestin2 (+βArr2 siRNA) or scrambled siRNA (+Scr siRNA) for 18 h. Cells were rinsed with serum free media prior to treatment with morphine, DAMGO, herkinorin, and capsaicin as in A and B. **,*** p<0.01, 0.001 by two-way ANOVA. E, F) TG neurons from rats were nucleofected with MOPr-GFP, and pretreated with the PKA inhibitor, H89 (20 μM), 5 min before treatment with morphine, DAMGO, herkinorin, and capsaicin as in A and B.