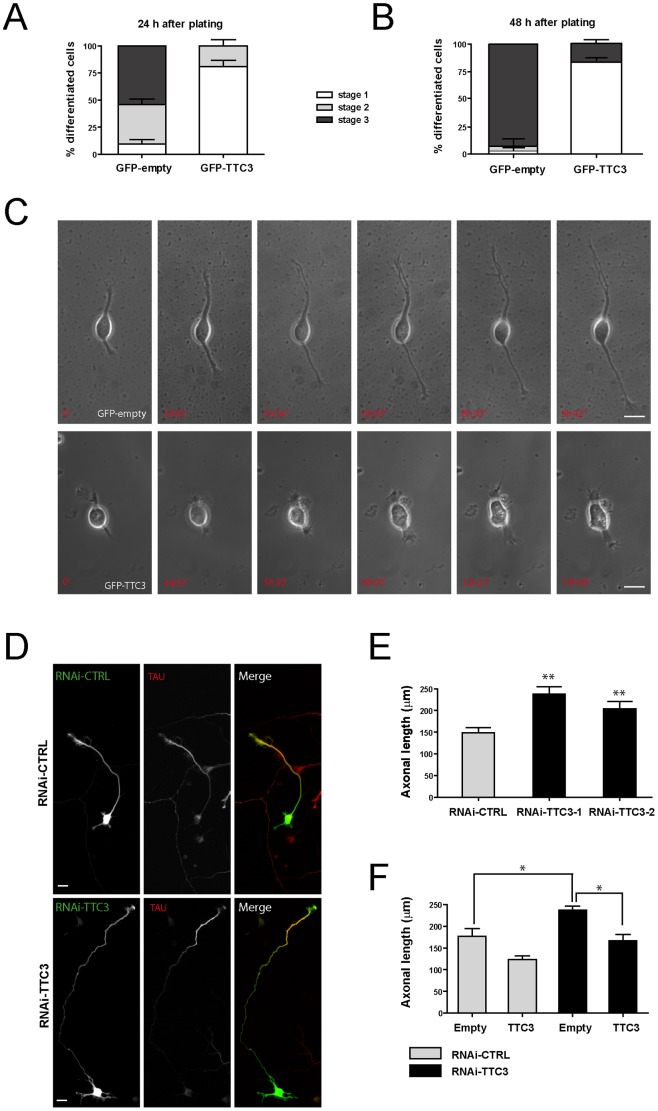
Figure 1. Effects of altered TTC3 levels on neuronal differentiation.
A–B. Hippocampal neurons extracted from E18.5 rats were electroporated by nucleofection with the indicated plasmids. 24 hours (A) or 48 hours (B) after plating, cells were processed for immunofluorescence and the morphology of GFP-positive cells was assessed to analyze their distribution across the indicated differentiation stages. C. Selected frames from time-lapse series of neurons transfected as in panel A, undergoing differentiation in culture. For full movies, see supporting material. D–E. Hippocampal neurons were nucleofected with control or TTC3-specific sh-RNA-expressing plasmids, plated and allowed to differentiate 72 hours in culture. Cells were then processed for IF with anti-Tau antibodies and the axonal length was then quantified with ImageJ. F. Overexpression of GFP-TTC3 (TTC3) is able to rescue the phenotype induced by TTC3 downregulation. Cells were co-electroporated with sh-RNA-expressing plasmids together with GFP-empty (empty) or GFP-TTC3 (TTC3). After 72h, cells were than analyzed as in panel E. Scale bars = 10 μm; error bars = Standard Error of the Mean (SEM); *P<0.05, **P<0.01, two tails Student T-test.