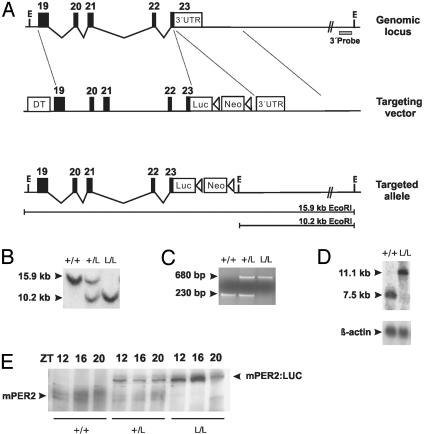
Fig. 1.
Generation of mPer2Luc knockin mice. (A) Diagram of the mPer2 locus, targeting vector, and targeted knockin allele. Exons are indicated by filled blocks with numbers. E, EcoRI; DT, diphtheria toxin A chain; Neo, neomycin resistance gene; triangle, loxP site. (B) Southern blot of DNA from F2 animals after digestion with EcoRI. The 600-bp 3′ external probe (A) detects a 15.9-kb WT fragment and a 10.2-kb targeted fragment. + indicates WT; L indicates luc knockin allele. (C) PCR genotyping of F2 animals. Agarose gel electrophoresis reveals the presence of a 230-bp WT (+) allele and a 680-bp knockin allele (L). (D) Northern blot of total RNA extracted from mouse brain probed with a 1.4-kb mPer2 partial cDNA fragment. In contrast to the 7.5-kb WT (+) allele, the larger 11.1-kb band represents the transcript from the targeted (L) allele. (E) Western blot of WT (+/+), mPer2Luc heterozygote (+/L), and homozygote (L/L) mouse.