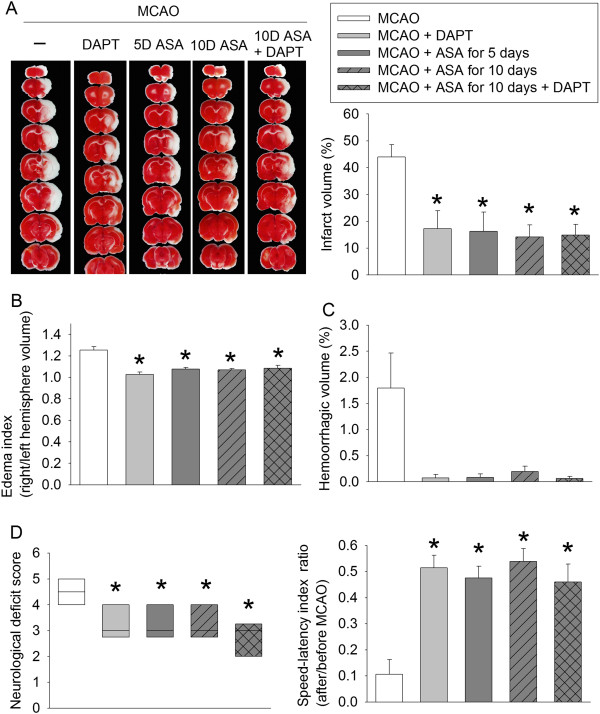
Figure 6.
Aspirin and DAPT-induced neuroprotection. Rats received various aspirin treatments around or immediately after a 90-minute middle cerebral arterial occlusion (MCAO). Intracerebroventricular injection of N-[N-(3,5-Difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl ester (DAPT) was performed immediately after the MCAO. The results were evaluated at 3 days after the MCAO. (A) Brain slices stained with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride from representative mice and percentage of brain infarct volume in ipsilateral hemisphere volume. (B) Edema index. (C) Percentage of hemorrhagic volume in ipsilateral hemisphere volume. (D) Left panel shows the neurological deficit scores evaluated immediately before the animals were euthanized for the assessment of infarct sizes (data are presented in panel A). ●, Lowest or highest score (the score will not show up if it falls in the 95% interval); between lines, 95% interval of the data; inside boxes, 25-75% interval including the median of the data. Right panel shows the performance on rotarod. Rats were tested before and 3 days after the MCAO and the speed–latency index ratio of these two tests are presented. All results except for those in the left panel of panel D are the means ± SEM (n = 6). *P < 0.05, compared with the animals subjected to MCAO only. ASA, acetylsalicylic acid.