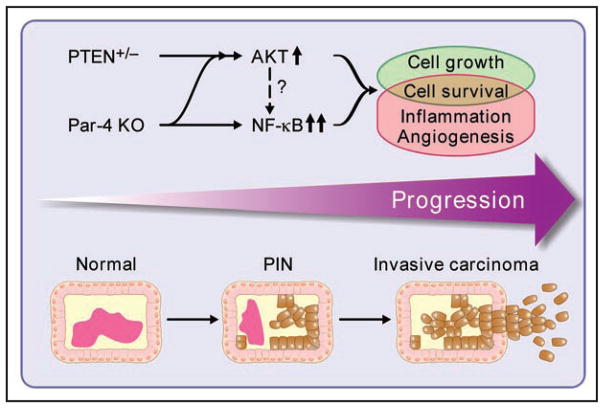
Figure 1.
Cooperation of Par-4 deficiency and PTEN haploinsufficiency in prostate cancer progression. Par-4 loss cooperates with PTEN heterozygosity to promote invasive prostate carcinoma. The simultaneous inactivation of Par-4 and PTEN enhances Akt and leads to a synergistic stimulation of the NFκB pathway. This sets in motion complementary signals regulating cell growth, cell survival, inflammation and angiogenesis that collaborate in prostate cancer progression. It is not known whether Akt is able to directly impinge on the NFκB pathway in this system.