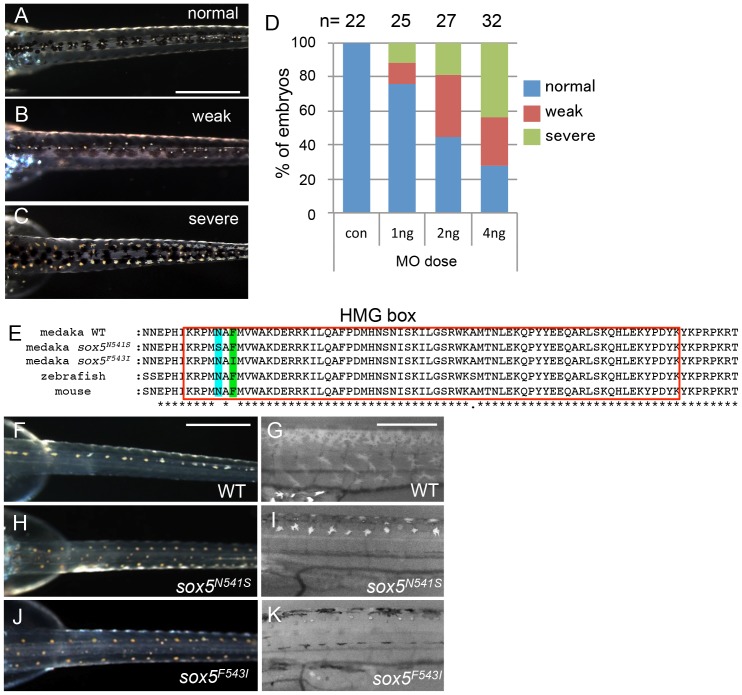
Figure 4. sox5 morphant and allelic TILLING mutants show the ml-3 pigment phenotype.
(A–D) Injection of sox5 MO into WT embryo generates ml-3 mutant phenocopies with increased leucophores in the dorsal trunk compared with embryos injected with the control MO which all show a WT leucophore phenotype (A). The severity of the leucophore phenotype is classified into “weak” (B) and “severe” (C). In “weak” embryos, the majority of leucophores are located along the midline of the trunk, while fewer leucophores are ectopically positioned (B). “Severe” embryos show a phenotype indistinguishable from that of ml-3 (C). In most cases, general morphology is normal, although about half of sox5 morphants combined a “severe” pigment phenotype with many ectopic leucophores with gross morphological abnormalities (data not shown). (D) Using this phenotypic classification, we scored the severity of the ml-3 morphant phenotypes at three different doses (1 ng, 2 ng and 4 ng) and with control MO (con). The number of injected embryos is indicated above the bars (n). (E) Our TILLING screen for sox5 mutant alleles identified two distinct mutations causing amino acid substitutions at N541S (blue box) or F543I (green box) respectively in the HMG domain (red boxed). (F–K) Homozygotes for the TILLING mutations (sox5N541S and sox5F543I) are compared with WT siblings (F, G). These sox5 mutants exhibit ml-3 mutant phenocopies as manifested in ectopic and excessive formation of leucophores and complete absence of xanthophores. Leucophores are shown in the darkfield image (H, J). Xanthophores are not detectable under UV light (I, K). Scale bars: 500 µm.