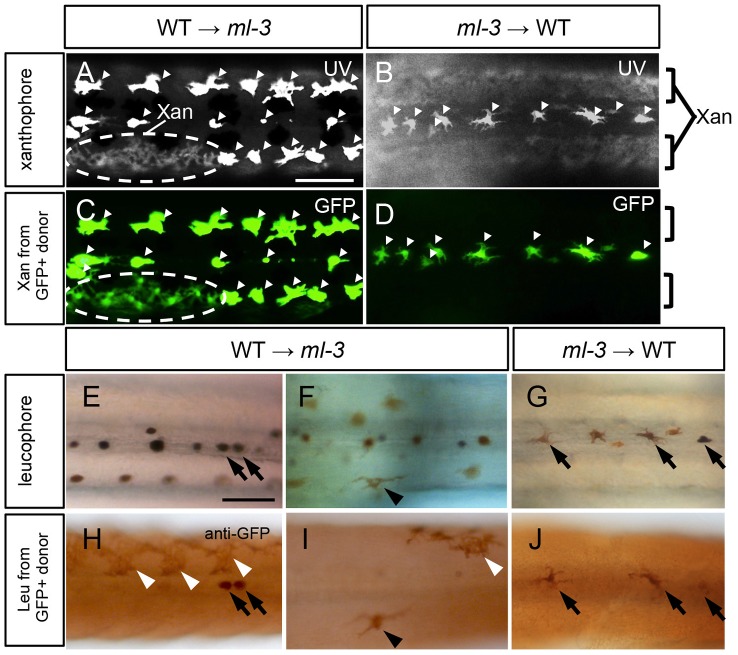
Figure 6. Cell transplantation.
(A, C, E, F, H, I) Transplants of WT donor cells into ml-3 hosts. (B, D, G, J) Transplants of ml-3 mutant donor cells into WT hosts. (A–D) Note that leucophores are fluorescent through both UV and GFP filters (white arrowheads) and xanthophores are fluorescent through UV filter but not through GFP filter. In both types of transplant experiments, xanthophores and leucophores express GFP when generated from donor cells having slc2a15b:GFP transgene, but in leucophores the GFP signal is masked by strong auto-fluorescence of these cells. However, GFP expression is readily detectable by immunostaining (see Figures S5A–S5C). (A, C) In WT→ml-3 transplants, ectopic leucophores are partially lost and instead a patch of xanthophores (marked with dotted circle) positive for UV (A) and GFP (C) fluorescence can be seen. (B, D) In ml-3→WT transplants, leucophores and xanthophores develop and are positioned normally although leucophores derived from donor cells cannot be identified because GFP fluorescence is masked by strong auto-fluorescence. No xanthophores show GFP fluorescence (compare UV image, B and GFP image, D). (E, H) In one of WT→ml-3 transplants, a few GFP positive leucophores are found along midline (black arrows). (F, I) In another WT→ml-3 transplants, leucophores are ectopically formed and positive for GFP (black arrowheads). White arrowheads represent donor-derived xanthophores detected by anti-GFP antibody. (G, J) In ml-3→WT transplants, GFP-positive leucophores develop and are positioned normally along midline (black arrows). All images are dorsal views at 7 dpf. Xan, xanthophore; Leu; leucophore. Scale bars: 100 µm.