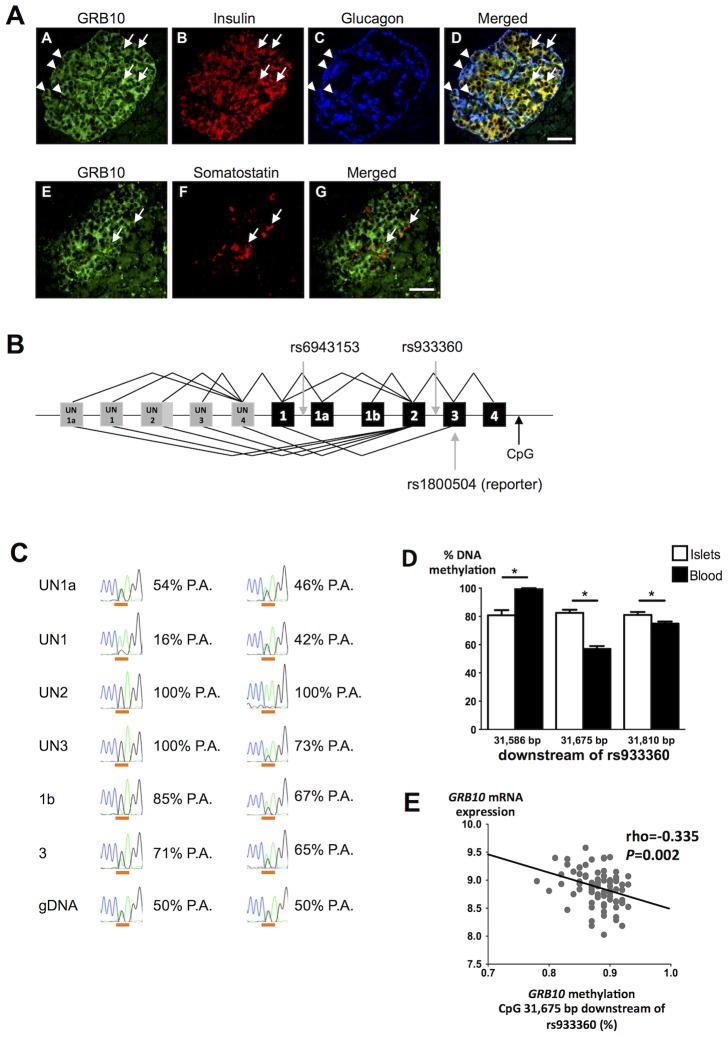
Figure 3. GRB10 expression in human islets.
(A) Immunostainings demonstrating that GRB10 (green, panel A, E) is abundantly expressed in β- (panel B, D), α- (panel C, D) and δ-cells (panel F, G) in human pancreatic islets. Arrows indicate co-localization with insulin (panel D) and somatostatin (panel G). Arrowheads indicate co-localization with glucagon (panel D). Scale bar = 50 µm. (B) Schematic representation of the GRB10 gene and SNPs investigated in the present study. Grey boxes = untranslated exons. Black boxes = translated exons. (C) Examples of RT-PCR on islet cDNA (top six rows) and PCR on genomic DNA (gDNA, bottom row) from two individuals heterozygous for the reporter SNP rs1800504. The first column states the forward primer location of each PCR and a forward primer in exon 3 captures all transcripts. The peaks show the Sanger sequencing trace across rs1800504, which is underlined (A: green trace, G: black trace). Percentages indicate the contribution from the paternal allele (P.A.) (G-allele in the first case, A-allele in the second case). The paternal genotype is identified assuming complete maternal imprinting of the UN2 promoter, in line with previous findings [12]. A sequence of heterozygous genomic DNA (gDNA) is shown on the bottom for comparison (50%-50%). (D) To study if DNA methylation of GRB10 is tissue-specific, the degree of methylation was analyzed at 3 CpG sites located ∼31.7 kb downstream of rs933360 in both human pancreatic islets of 98 donors and PBL from 6 trios using EpiTYPER. The exact position of each analyzed CpG site in relation to rs933360 is given in the figure. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p<0.05 for difference in methylation between human islets and PBL. (E) The GRB10 mRNA levels correlated negatively with the degree of methylation at the CpG site located 31,675 bp downstream of GRB10 rs933360.