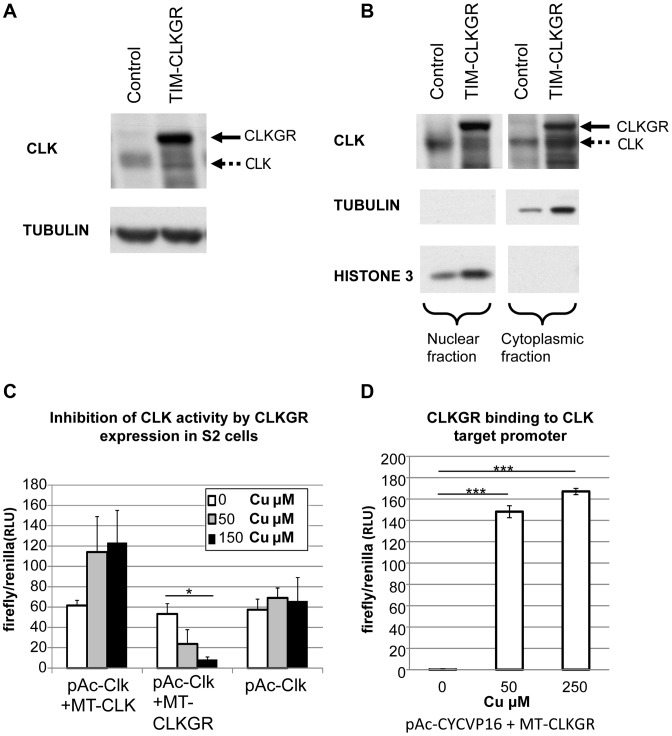
Figure 2. CLKGR is present in the nucleus, and competitively inhibits CLK function.
A. CLKGR protein is expressed in large amounts in TIM-CLKGR flies. Western blot from fly heads collected at CT15 using an anti-CLK antibody. The assay was performed from TIM-CLKGR flies and control flies (tim-gal4/+). Arrows indicate CLK or the CLKGR fusion protein, which can be distinguished by their size. B. CLKGR is present in both the nuclei and cytoplasm in TIM-CLKGR flies. Western blot from nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts of control (tim-gal4/+) or TIM-CLKGR fly heads collected at CT15. TUBULIN staining is shown as negative control for the nuclear fraction separation and positive control for the cytoplasm fraction. HISTONE-3 staining is shown as positive control for nuclear separation and negative control for the cytoplasm separation. C. CLKGR expression can inhibit CLK-mediated activity in Drosophila S2 cells. Drosophila S2 cells were transfected with vri-luciferase reporter plasmid, pAc-CLK plasmid, a plasmid that express CLK or CLKGR under regulation of a copper inducible promoter (metallothionein; MT-CLK or MT-CLKGR respectively), and a plasmid used for controlling transfection efficiency (pCopia-Renilla). No copper or two different amounts of copper were utilized as indicated in the graph. Experiment was done at three separate biological repeats. Plot shows average values of biological duplicates of one representative experimental repeat. Error bars represent standard deviation. One-way Anova was performed to determine statistical significance. *p<0.05. D. CLKGR can bind to CLK targets promoters. We induced CLKGR expression in S2 cells using the MT-CLKGR plasmid; in parallel to constant expression of CYCVP16 (from the pAc-CYCVP16 expressing plasmid). CYCVP16 and CLKGR together activate CLK-driven transcription suggesting they bind to CLK targets promoters. Experiment was done at three separate biological repeats. Plot shows average values of duplicates of one representing repeat. Error bars indicate standard deviation. CLK-target activity was measured using a vri-luciferase reporter and values were normalized to a transfection control (pCopia-Renilla). T-test was performed to determine statistical significance between time points. ***p<0.001.