Figure 5. HBZ inhibits Rex-mediated nuclear export of intron-containing mRNAs.
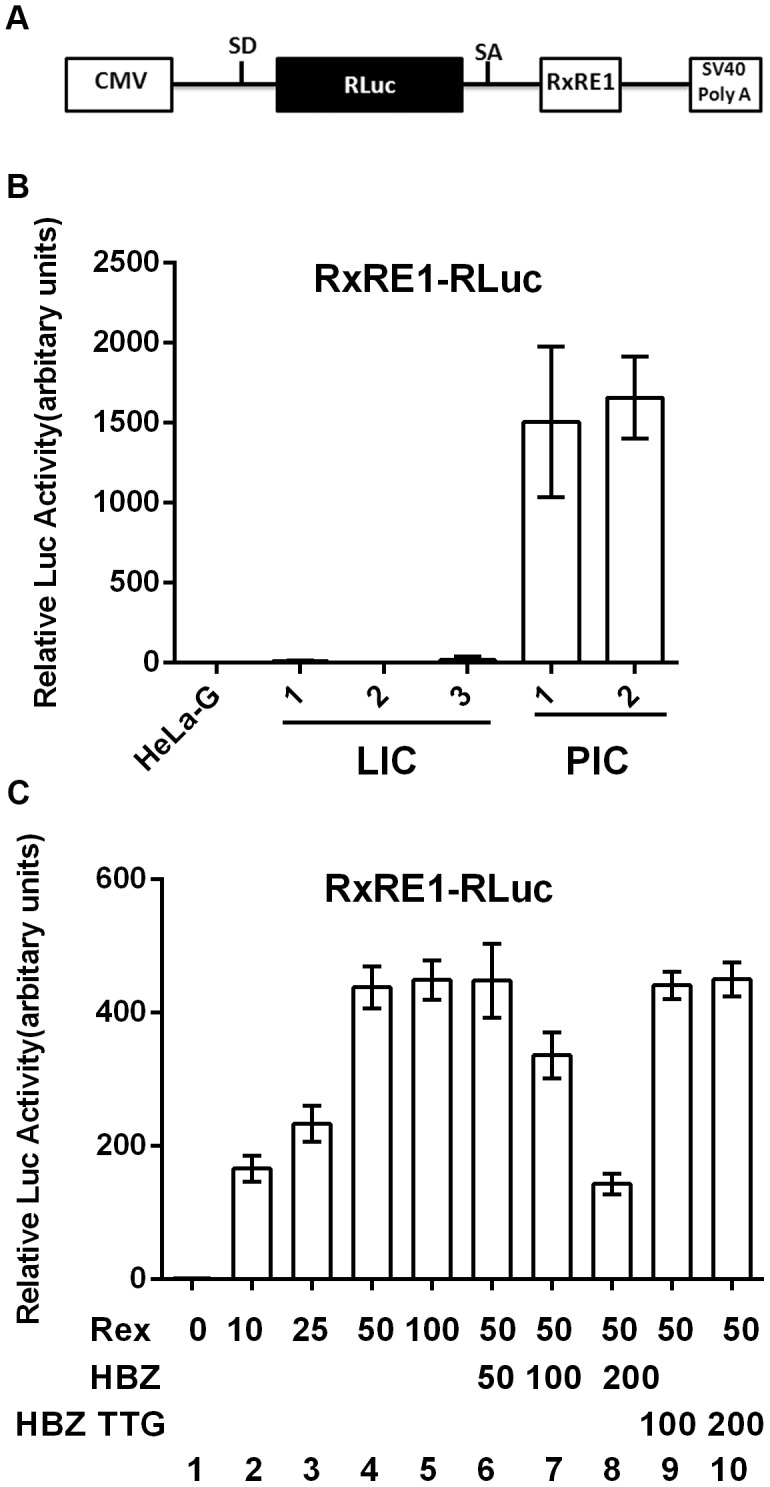
(A) Schematic representation of the Rex reporter construct, RxRE1-RLuc. CMV, cytomegalovirus immediate early enhancer/promoter; SD, splice donor; Rluc, Renilla luciferase; SA, splice acceptor; RxRE1, HTLV-1 Rex-response element; and SV40 poly A, polyadenylation site of the SV40 early gene. (B) Rex activities in HeLa-G, latently infected cell (LIC) clones 1–3, and productively infected cell (PIC) clones 1 and 2. Cells of each clone were transfected with 200 ng RxRE1-Rluc and 20 ng of PGL3-firefly-Luc (PGL3-Luc) for 48 hours. Dual luciferase assay was performed as in Materials and Methods . Relative luciferase activities were determined by calculating Rluc/Luc ratios followed by normalizing against that ratio of HeLa-G control. Mean luciferase activity ±standard deviation from three experiments is plotted. (C) Dose-dependent inhibition of Rex activity by HBZ. HeLa-G cells were co-transfected with 200 ng RxRE1-Rluc and 20 ng PGL3-Luc together with the indicated amount of Rex and HBZ expression constructs. Dual luciferase assay was performed as in (B). Lanes 1–5, dose-dependent titration of Rex. Lanes 6–8, dose-dependent inhibition of the Rex activity by wild-type HBZ. Lanes 9 and 10 contained the HBZ TTG mutant whose translational initiation codon ATG is mutated to TTG.
