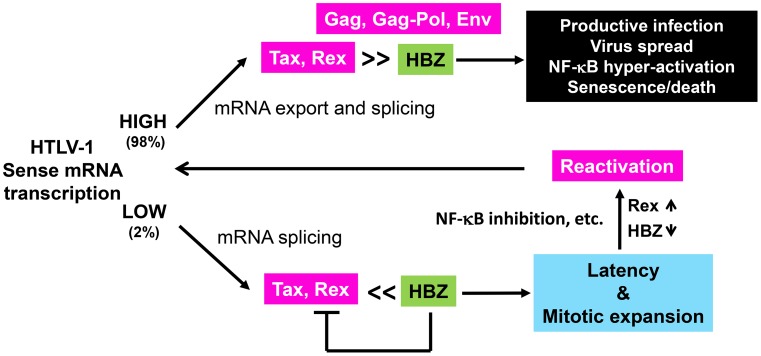
Figure 7. Alternative outcomes of HTLV-1 infection.
Most HTLV-1-infected cells express Tax and Rex strongly. Under this condition, HBZ is insufficient to block the activities of Tax and Rex. As such, HTLV-1 structural proteins are abundantly expressed and viral particles are produced. In these cells, Tax chronically activates NF-κB, which triggers a cellular senescence response. A small fraction of HTLV-1-infected cells harbor latent proviral DNA. The levels of Tax/Rex expression are low in these cells. LTR trans-activation and senescence induction by Tax, along with viral mRNA nuclear export by Rex are inhibited by HBZ. As such, no viral structural proteins are expressed and these latently infected cells undergo mitotic expansion possibly driven by Tax and HBZ. Latent HTLV-1 provirus can be reactivated by down-regulation of HBZ, up-regulation of Rex, and strong inhibition of NF-κB.