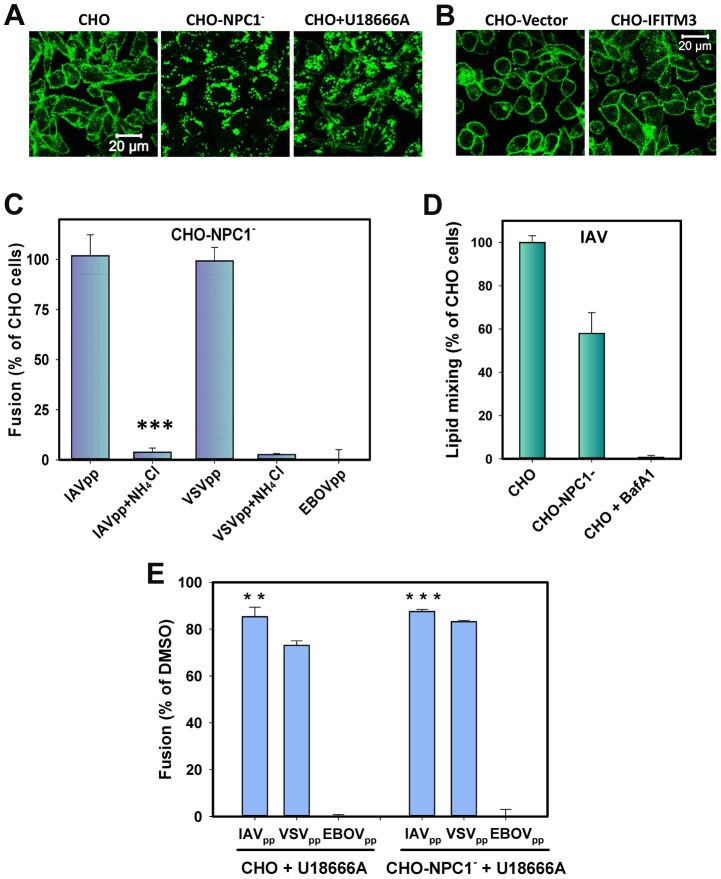
Figure 7. Cholesterol accumulation in endosomes of CHO cells does not inhibit viral fusion.
(A) Filipin staining of untreated and U18666A-treated (40 µM) CHO cells and of CHO-NPC1− cells devoid of NPC1. (B) Filipin staining of CHO-Vector and CHO-IFITM3 cells. Images in panels A and B show confocal sections through the middle of cells. (B) Confocal images of CHO-Vector and CHO-IFITM3 cells stained with filipin. (C) IAVpp (MOI = 2), VSVpp (MOI = 1) or EBOVpp (MOI = 2) were pre-bound to CHO or CHO-NPC1− cells in the cold, incubated at 37°C for 90 min, and the resulting fusion activity was measured by the BlaM assay. Results are plotted as the relative extents of fusion CHO-NPC1− cells after normalizing to fusion with CHO cells. Control experiments were carried out in 70 mM NH4Cl. Data are means and SEM from 3 triplicate experiments. (D) The frequency of lipid mixing in CHO (n = 576) and CHO-NPC1− cells (n = 1241). Pre-treatment with 0.2 µM BafA1 for 30 min followed by initiation with imaging buffer containing BafA1and 70 mM NH4Cl inhibited the fusion activity: only 4 out of 1532 particles underwent lipid mixing. Error bars are standard deviations from at least 4 experiments. (E) Pretreatment of CHO cells with U18666A (40 µM, 8 h) modestly diminishes IAVpp or VSVpp fusion and abrogates EBOVpp fusion, as measured by the BlaM assay. Data are means and SEM from 2 triplicate experiments. ***, P<0.001; **, P<0.02.