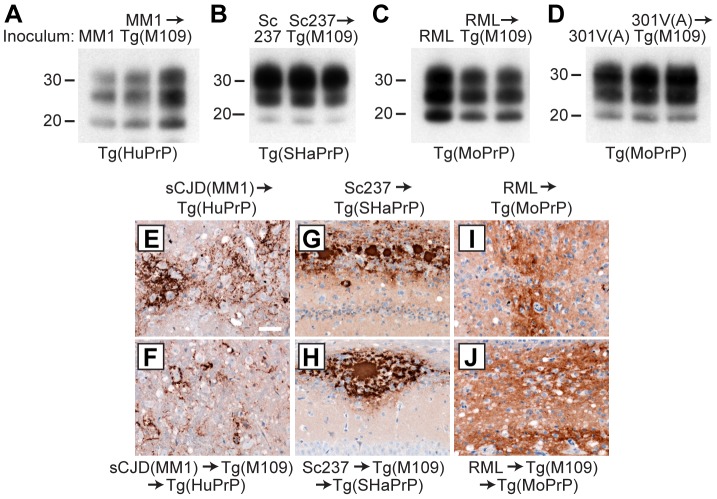
Figure 4. Analysis of PK-resistant PrPSc and cerebral PrPSc deposition following retrotransmission of Tg(M109)-passaged prion isolates.
Following retrotransmission of Tg(M109)-passaged prion isolates, the biochemical characteristics (A–D) and deposition patterns (E–J) of PrPSc were similar. sCJD(MM1) (A, E, F); Sc237 (B, G, H); RML (C, I, J); and 301V(A) (D) prions were respectively injected into Tg(HuPrP), Tg(SHaPrP), Tg(MoPrP), and Tg(MoPrP) mice. The same inocula were also passaged once in Tg(M109) mice, then injected into the same respective lines. In the immunoblots, the electrophoretic mobility and glycosylation profile are identical in mice infected with the original inoculum and with the inoculum passaged in Tg(M109) mice. Each of the duplicate lanes for the retrotransmission samples represents an individual mouse. PK-resistant PrPSc was detected using the antibody HuM-P. In the micrographs, PrPSc was detected in the brainstem using antibody 3F4 (E–F) and in the hippocampus using antibody HuM-D18 (G–J). In panels A–D, molecular weight measurements are shown in kDa. Scale bar in E represents 50 µm and applies to panels F–J.