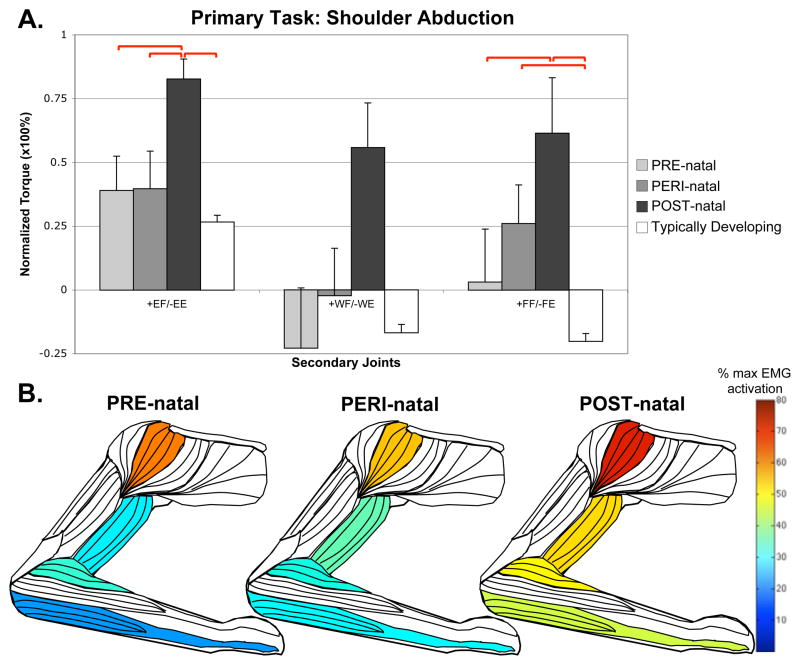
Figure 1.
Secondary torques associated with the primary torque direction task of shoulder abduction, with standard error bars. A significant effect of group-limb was found in the elbow (F=2.902, p=0.016) and fingers (F=3.138, p=0.010). Significant post-hoc comparisons, where p<0.05, are shown with red bars above the graph. Also shown are muscles colored to represent percentages of maximal EMG activity where differences were found between groups. These muscles include middle deltoid (Kruskal-Wallis, H=15.979, p=0.025), biceps brachii (ANOVA, F=2.201, p=0.056), brachioradialis (ANOVA, F=1.923, p=0.093) and combined wrist and finger flexors (ANOVA, F=3.097, p=0.011).