FIGURE 2.
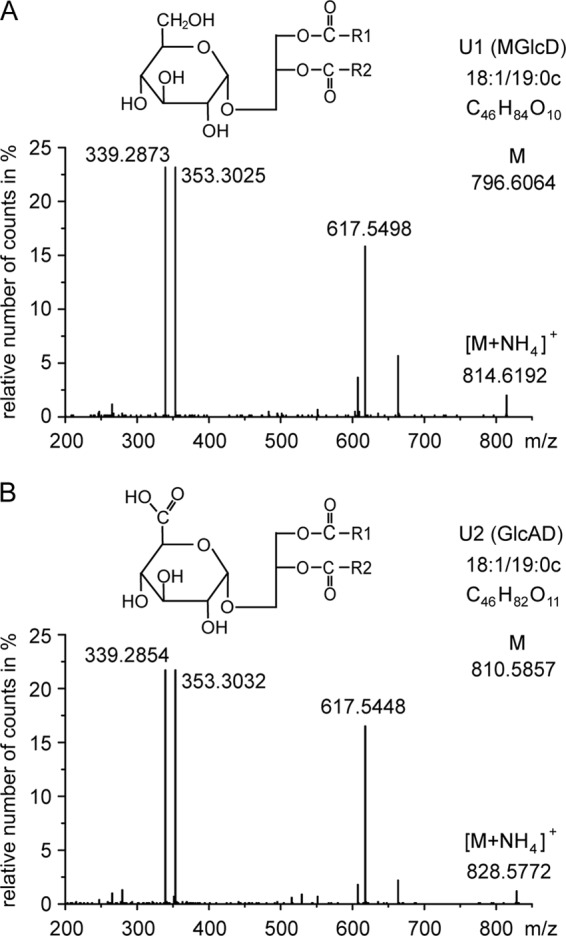
Q-TOF MS/MS spectra of monohexosyl diacylglycerol (U1) and monohexuronosyl diacylglycerol (U2). Parental ions (as ammonium adducts) of one main molecular species of U1 (calculated m/z 814.6403) and U2 (calculated m/z 828.6196) were selected in the positive mode (with a detection window of m/z 1.2) and fragmented. The fragments with m/z 617.5498 (or 617.5448) represent DAG-18:1/19:0c (as protonated form with loss of H2O). The neutral loss of 197.0905 (m/z 814.6403 minus 617.5498) is derived from hexose (as ammonia adduct); the neutral loss of 211.0748 (m/z 828.6196 minus 617.5448) is derived from hexuronic acid (as ammonia adduct). The ions m/z 339.28 and 353.30 represent monoacylglycerol-18:1 and monoacylglycerol-19:0c, respectively (each as protonated form with loss of H2O). COO-R1 and COO-R2 represent two different fatty acyl residues (18:1 or 19:0c) bound to the glycerol back bone. The headgroup structures of U1 (MGlcD) and U2 (GlcAD) were further determined by NMR containing α-glucose or α-glucuronic acid, respectively, as illustrated in the figure.
