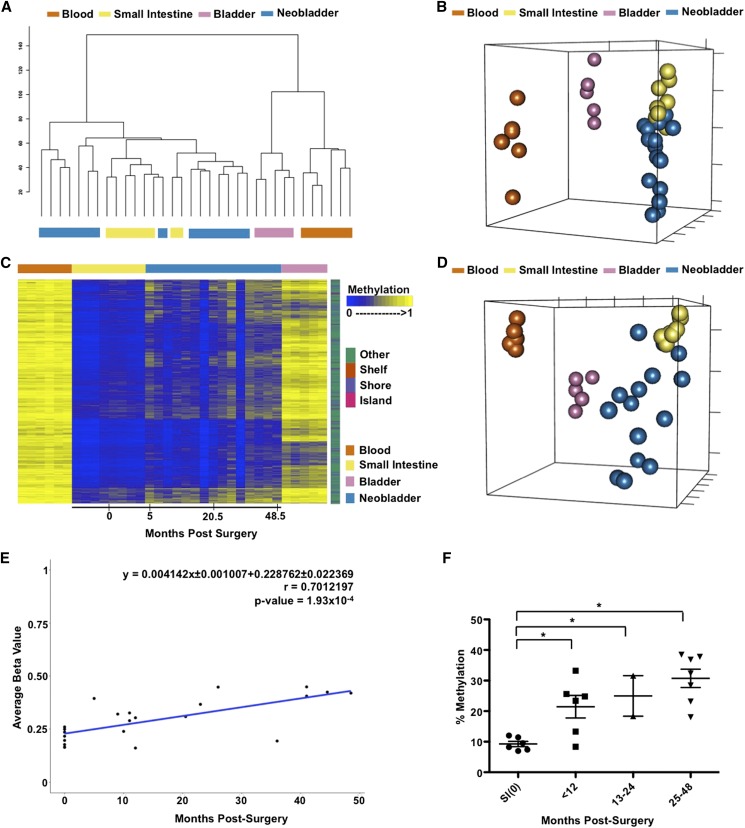
Figure 2.
DNA methylation changes in the neobladder is a dynamic process. (A) Dendrogram of hierarchical clustering performed on a single Euclidean distance for normal blood, small intestine, bladder, and neobladder samples shows the relationship between each tissue type. Neobladder samples cluster closer to the small intestine than to the control bladder and blood. (B) Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (MDS) plot using all HM450 probes for all samples shows distinct separation between normal small intestine, blood, and bladder (Kruskal’s stress = 0.0334). Each axis represents one dimension. Although the neobladder samples cluster closer to the small intestine control, many have diverged away, suggesting alterations in DNA methylation of intestinal epithelial cells post-surgery. (C) A heat map showing intestine-specific unmethylated probes that have significant (Benjamini-Hochberg adjusted P-value < 0.05) linear regression value (n = 4162). Neobladder samples are arranged from the earliest to the latest time points post-surgery (0–48.5 mo) and show increased methylation over time. (D) Nonmetric MDS plot using the cluster of probes that gain methylation in the neobladder illustrates the distinctiveness of neobladder samples from each other in comparison to the normal tissue controls that cluster tightly together based on their respective cell type (Kruskal’s stress = 0.0098). (E) The rate of de novo methylation in the neobladder was measured for individual probes and as an average of the cluster shown in C, and Pearson’s correlation (r) was calculated to show that changes in DNA methylation in the neobladder are time dependent. Time 0 refers to normal small intestine tissues collected before being transplanted into a bladder environment. (F) Pyrosequencing of REG4, an intestine-specific gene, validates the global finding that there is a significant time-dependent methylation increase of intestine-specific unmethylated probes in the neobladder. T-test was performed. (*) P-value < 0.05.