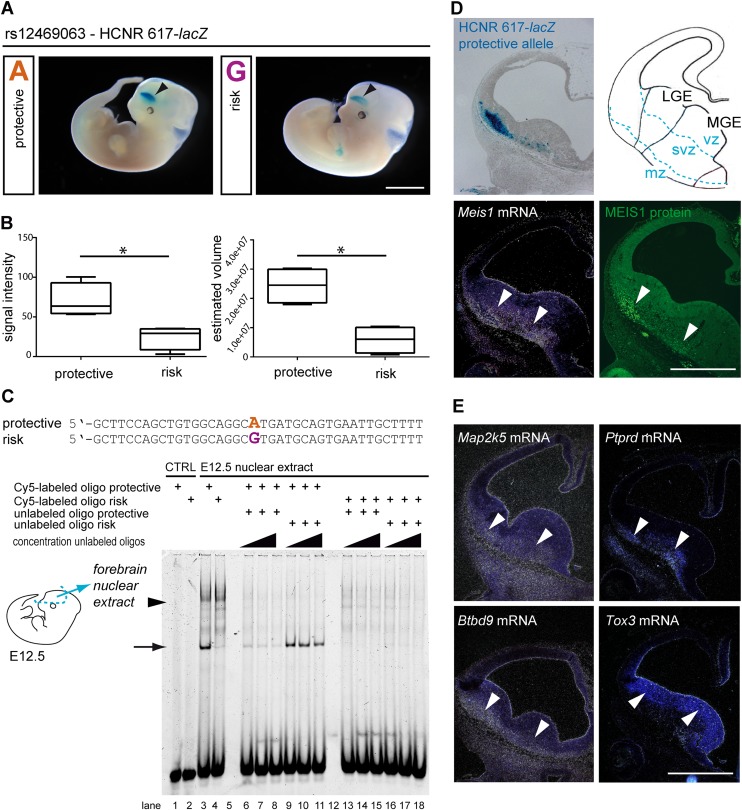
Figure 3.
In vivo and in vitro identification of allele-specific HCNR 617 enhancer function in the ganglionic eminences of the mouse. (A) Representative transgenic mouse embryos after pronucleus injection of HCNR 617 protective (left) and risk allele constructs (right) at stage E12.5. Blue color indicates regions expressing the reporter gene beta-galactosidase (lacZ). Arrowhead indicates the reproducible telencephalic signal (bar represents 2.5 mm). (B) Analysis of the signal intensity in Theiler-staged embryos (stages 19 and 20; nprotective = 4, nrisk = 4) showed a reduction down to 35% (Wilcoxon rank sum test, P = 0.029). Stereological volume estimation according to Cavalieri revealed a significant volume reduction down to 24% for the risk allele (Wilcoxon rank sum test, P = 0.029). (C) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay using oligonucleotides encompassing rs12469063 showed allele-specific differences of DNA-protein complex formation using E12.5 forebrain nuclear extract (lanes 3 and 4, arrow and arrowhead). Specificity is proven by competition with unlabeled risk and protective oligonucleotide in excess (lanes 6–18). CTRL, control (no protein). (D) Frontal sections through the forebrain reveal lacZ reporter activity in the mantle zone (mz) of the ganglionic eminences, in the same region as Meis1 transcript and MEIS1 protein (arrowheads; bar represents 500 µm); no transcripts are visible in the ventricular (vz) and subventricular (svz) zones. (E) Transcripts of all additional GWAS-RLS risk loci map to the embryonic ganglionic eminences. mRNA of Ptprd, Btbd9, and Map2k5 was detected in the mantle zone (mz) of the LGE and MGE. Tox3 was expressed in the adjacent ventricular (vz) and subventricular (svz) zone (arrowheads; bar represents 500 µm).