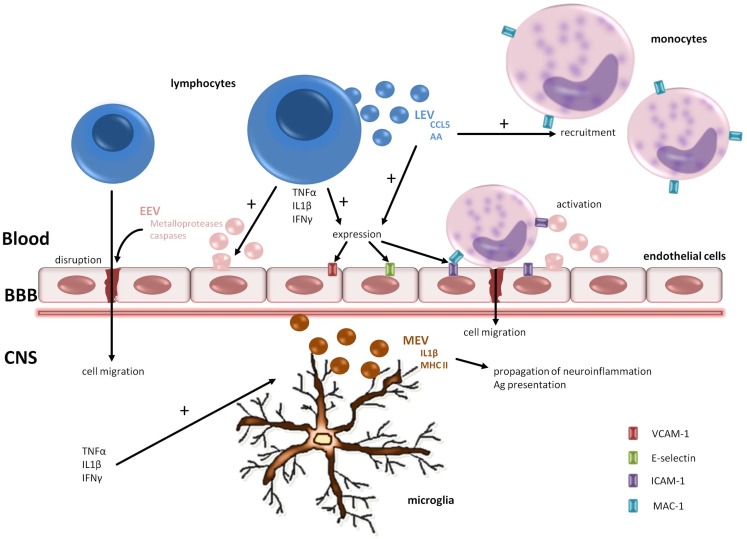
Figure 2.
Pathogenic roles of EV in MS. EVs are involved in the transendothelial cell migration of lymphocytes and monocytes and the spread of neuroinflammation. Metalloproteases carried by EEVs promote BBB disruption. The release of proinflammatory cytokines from lymphocytes augments adhesion molecules on endothelial cells facilitating cell adhesion. In the CNS compartment, microglia play a key role in propagation of neuroinflammation shedding MEVs containing IL1-b and MHC-II. BBB, blood–brain barrier; CNS, central nervous system; AA, arachidonic acid; EEV, endothelial-derived extracellular vesicle; LEV, leukocyte-derived extracellular vesicle; MEV, microglia-derived extracellular vesicle.