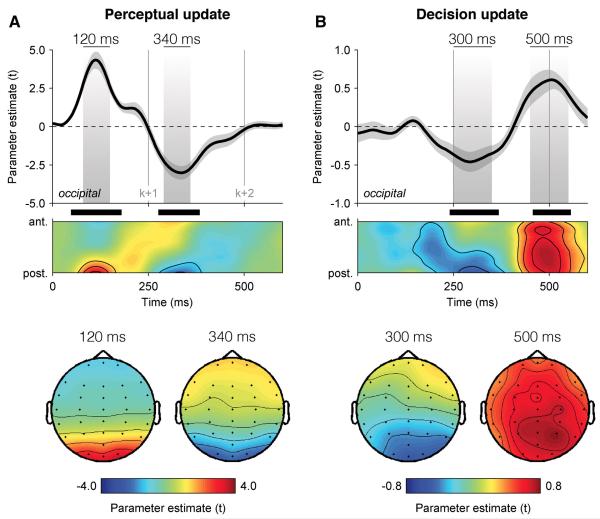
Figure 2. Dissociable neural encoding of perceptual and decision updates.
(A) Neural encoding of perceptual update PUk in EEG signals, expressed as parameter estimate in t units. Upper panel: encoding time course at occipital electrodes (above), and following a spatial antero-posterior gradient from electrode FPz to electrode Oz (below). Shaded areas highlight positive and negative components peaking respectively at 120 ms (left) and 340 ms (right) following element k. Lower panel: encoding scalp topographies at 120 ms (left) and 340 ms (right) following element k. Shaded error bars indicate s.e.m. Thick black lines indicate cluster-level significance at p < 0.001.
(B) Neural encoding of decision update DUk in EEG signals. Upper panel: encoding time course at occipital electrodes (above), and following the antero-posterior gradient (below). Shaded areas highlight negative and positive components peaking respectively at 300 ms and 500 ms following element k. Lower panel: encoding scalp topographies at 300 ms (left) and 500 ms (right) following element k. Same conventions as in (A).