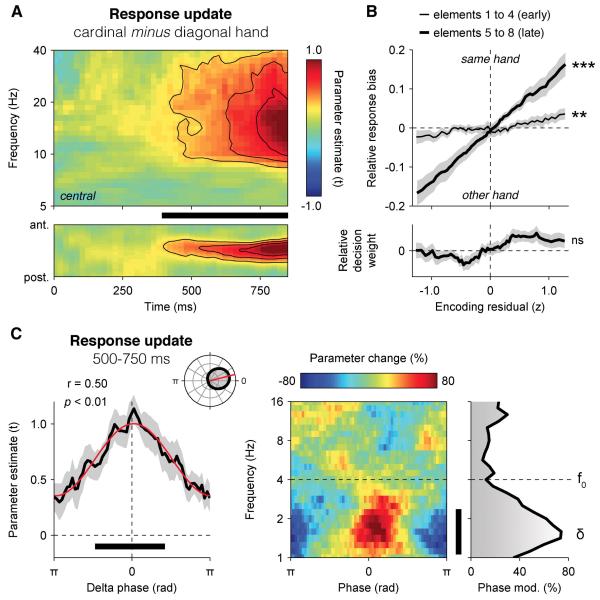
Figure 7. Neural encoding of the running decision variable in motor beta-band activity.
(A) Neural encoding of response update RUk in motor beta-band activity (10-30 Hz), expressed as parameter estimate in t units. Upper panel: encoding time-frequency profile at motor electrodes (above), and following the antero-posterior gradient (below). The thick black bar indicates cluster-level significance at p < 0.001.
(B) Relationship between encoding residuals in motor beta-band activity and the relative response bias (upper panel) or decision weight (lower panel) at 500-750 ms following early elements 1-4 (thin line) and late elements 5-8 (thick line). Shaded error bars indicate s.e.m. Two stars indicate a significant correlation at p < 0.01, three stars at p < 0.001, ns a non-significant correlation.
(C) Phase-dependent fluctuations in the neural encoding of response update RUk in motor beta-band activity (10-30 Hz). Left panel: relationship between the phase of parietal delta oscillations at 500 ms following element k and the encoding of RUk in motor beta-band activity at 500-750 ms. Right panel: relationship between the phase of parietal EEG oscillations from 1 to 16 Hz at 500 ms following element k and the neural encoding of response update RUk in motor beta-band activity. Same conventions as in Figure 4.