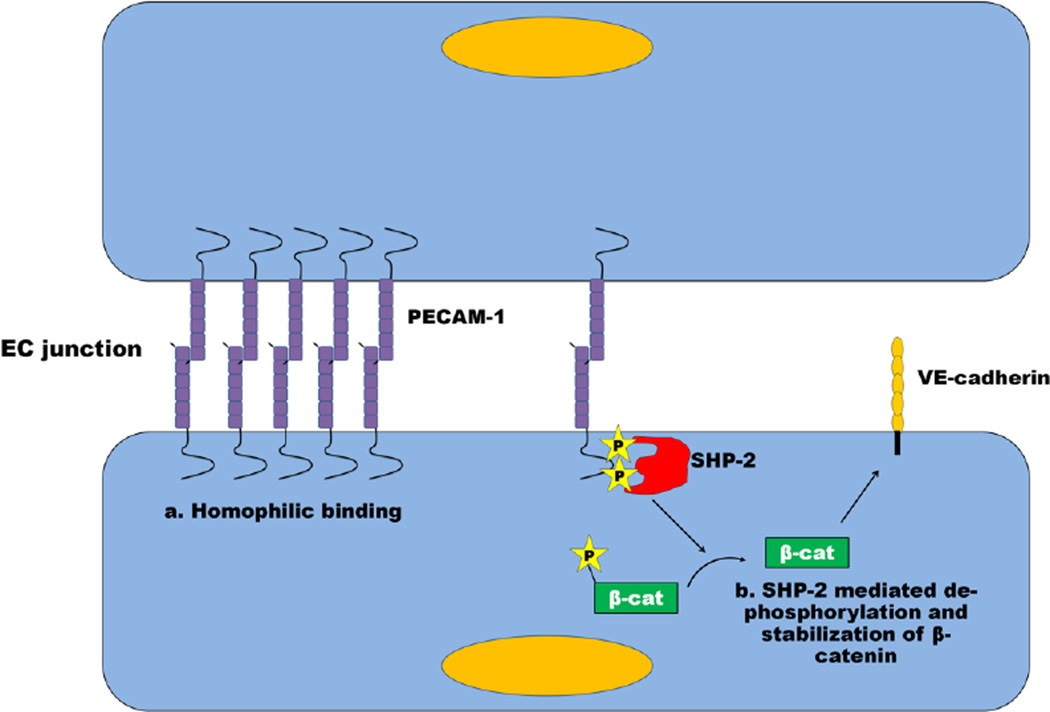
Fig. 3. Mechanisms by which PECAM-1 modulates paracellular permeability.
Homophilic PECAM-1/PECAM-1 interactions between neighboring endothelial cells have been demonstrated to localize PECAM-1 at the endothelial junction. These interactions have recently been shown to be more important than known signaling mechanisms for PECAM-1-mediated barrier protection. PECAM-1 has been shown in certain experimental systems to facilitate the dephosphorylation and stabilization of β-catenin through recruitment of SHP-2 to its ITIM, thus allowing β-catenin to re-associate with VE-cadherin, thus stabilizing the EC junction. In other experimental systems, the ability of PECAM-1 to fortify endothelial cell-cell junctions appears to be ITIM-, and therefore SHP-2, -independent. See text for details.