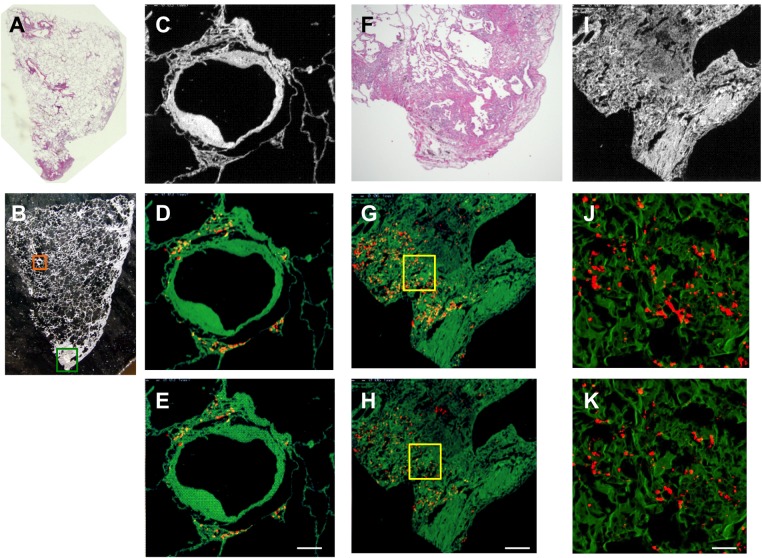
Figure 4.
Representative images of light micrographs and electron probe microanalyser with wavelength dispersive spectrometer (EPMA-WDS) of a lung specimen from case 10 with hard metal lung disease pathologically diagnosed as usual interstitial pneumonia pattern (A). (B,C) An arteriole and its surrounding interstitium (orange square) are elementally analysed by EPMA-WDS to demonstrate that (D) tungsten and (E) tantalum are distributed in the periarteriolar area with little fibrosis. Elemental analysis by EPMA-WDS of subpleural fibrosis with dense acellular collagen (green square in B, F and I) also shows (G and J) tungsten and (H and K) tantalum almost randomly distributed in magnified images (yellow squares in G and H are magnified to show (J) tungsten and (K) tantalum). We did not further analyse the centrilobular pattern or the cannibalistic giant cells shown in figure 3. Note that the distribution of tungsten is not exactly the same as that of tantalum. Original magnification, (A) panoramic view, (B) ×4. Scale bars for the magnification and scan areas for (E), (H) and (K) correspond to 100 μm (0.768×0.768 mm), 200 μm (1.536×1.536 mm) and 25 μm (0.1792×0.1792 mm), respectively.