Abstract
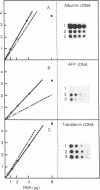
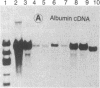
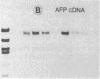
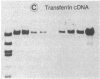
Steady-state levels of mRNAs were determined for the serum proteins albumin, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), and transferrin, as well as for aldolase B in livers of newborn mice homozygous for a radiation-induced lethal deletion (c14CoS) in chromosome 7. Deficiencies in synthesis and secretion of the serum proteins as well as in activities of certain liver-specific enzymes characterize these homozygotes. The results of RNA dot and gel-blot hybridizations with the respective cloned cDNA probes showed a decrease to one-fourth of aldolase B mRNA levels in homozygous mutant livers compared to normal littermates, in contrast to normal levels of mRNA sequences for the three serum proteins in the mutants. Furthermore, the mRNA sequences were shown to be present as mature mRNA molecules in both mutant and normal littermate livers. We suggest that the deficiencies of liver-specific serum proteins and those of the enzymes caused by the lethal deletions around the albino locus on chromosome 7 of the mouse are due to different causes. In the case of the liver-specific enzyme examined here--i.e., aldolase B--control at the level of transcription or of message stability is affected in the homozygous deletion mutants, whereas the deficiencies of serum proteins are not reflected on the mRNA level and owe their origin to an effect on a posttranscriptional or translational level. These results lend further support to the assumption that the deleted portion of the genome includes genes concerned with the control and regulation of liver cell differentiation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cori C. F., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S., Klinger H. P., Pick L., Schlagman S. L., Teicher L. S., Wang-Chang H. F. Complementation of gene deletions by cell hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):479–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cori C. F., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S., Shaw P. A., Robinson C. Correction of a genetically caused enzyme defect by somatic cell hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6611–6614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M., Ruddle F. H. Murine alpha-fetoprotein and albumin: two evolutionarily linked proteins encoded on the same mouse chromosome. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 May;7(3):289–294. doi: 10.1007/BF01538854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gal A., Nahon J. L., Sala-Trepat J. M. Detection of rare mRNA species in a complex RNA population by blot hybridization techniques: a comparative survey. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganoza M. C., Williams C. A. In vitro synthesis of different categories of specific protein by membrane-bound and free ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1370–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland R. C., Cori C. F. Protein synthesis with membrane-bound polysomes and albumin messenger RNA from livers of mutant mice. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Apr 13;36(1):29–35. doi: 10.1007/BF02354829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Genetic control of morphogenetic and biochemical differentiation: lethal albino deletions in the mouse. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahon J. L., Gal A., Frain M., Sell S., Sala-Trepat J. M. No evidence for post-transcriptional control of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in developing rat liver neoplasia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Elliott R. W., Brown J. A., Shows T. B. Mapping of aminoacylase-1 and beta-galactosidase-A to homologous regions of human chromosome 3 and mouse chromosome 9 suggests location of additional genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):235–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Dever J., Sargent T. D., Thomas K., Sell S., Bonner J. Changes in expression of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes during rat liver development and neoplasia. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2167–2178. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellem C. H., Frain M., Erdos T., Sala-Trepat J. M. Differential expression of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes in fetal tissues of mouse and rat. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellem C. H., Gal A., Sala-Trepat J. M. Selective detection of rat and mouse specific albumin and alpha-fetoprotein mRNA molecules under highly stringent hybridization conditions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 15;229(1):226–236. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. P., Besmond C., Cottreau D., Weber A., Chaumet-Riffaud P., Dreyfus J. C., Trépat J. S., Marie J., Kahn A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat L-type pyruvate kinase and aldolase B. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14576–14584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorndike J., Trigg M. J., Stockert R., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S., Cori C. F. Multiple biochemical effects of a series of x-ray induced mutations at the albino locus in the mouse. Biochem Genet. 1973 May;9(1):25–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00485588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Belayew A. Transcriptional control of the murine albumin/alpha-fetoprotein locus during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5254–5257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi K., Mukai T., Hidaka S., Miyahara H., Tsutsumi R., Tanaka T., Hori K., Ishikawa K. Rat aldolase isozyme gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6537–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan G., Frain M., Park I., Besmond C., Maessen G., Trépat J. S., Zakin M. M., Kahn A. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human transferrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91648-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]