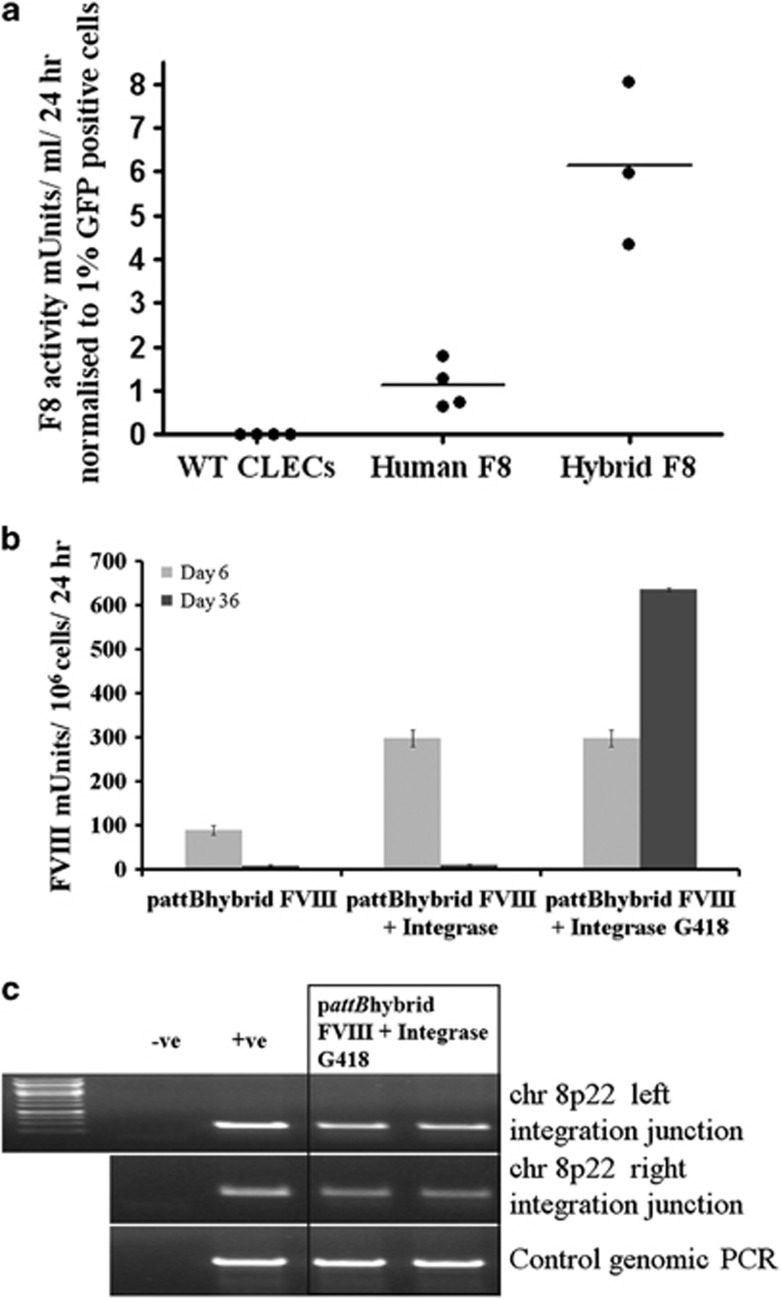
Figure 1.
Enhanced secretion of human–porcine hybrid BDD-FVIII and phiC31 integrase-mediated integration by transfected CLECs. (a) FVIII activity (Coamatic FVIII assay) in conditioned media of naive CLECs or CLECs co-electroporated with an enhanced green fluorescent protein reporter gene and either human BDD-FVIII F309S cDNA or human–porcine hybrid BDD-FVIII cDNA. Data are expressed as mU ml–1 per 24 h normalized to transfection efficiency. Each data point shows the mean of triplicate assays of a single experiment. An average 5.5-fold increase in FVIII levels (P=0.003; Student's unpaired t-test) was secreted by the hybrid FVIII cDNA compared with human FVIII cDNA. (b) FVIII activity of overnight conditioned media of three groups of electroporated CLECs: (i) pattBhybrid FVIII, no G418 selection; (ii) pattBhybrid FVIII+Integrase, no G418 selection; and (iii) pattBhybrid FVIII+Integrase with G418 selection. Conditioned media was collected on day 6 (before G418 selection) and day 36 (after G418 selection; where indicated) post-electroporation. Data are mean±s.e.m.; n=3 per group. (c) Genomic DNA (200 ng) extracted from a bulk population of genome-modified CLECs was amplified with primer pairs specific for the vector and chromosome 8p22 to detect the presence of left and right integration junctions indicative of correct integration at the pseudo attP site in 8p22 (done in duplicates). ‘–ve' denotes minus template PCR amplification while ‘+ve' denotes amplification from genomic DNA isolated from a clonal line of CLEC previously identified to have integration at 8p22. Control PCR amplified a 900-bp region in 19q13.42 (AAVS1 locus). Amplified products were resolved by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and imaged using BioRad Gel Doc 2000 transilluminator and QuantityOne software (Bio-Rad Laboratories).