Figure 1.
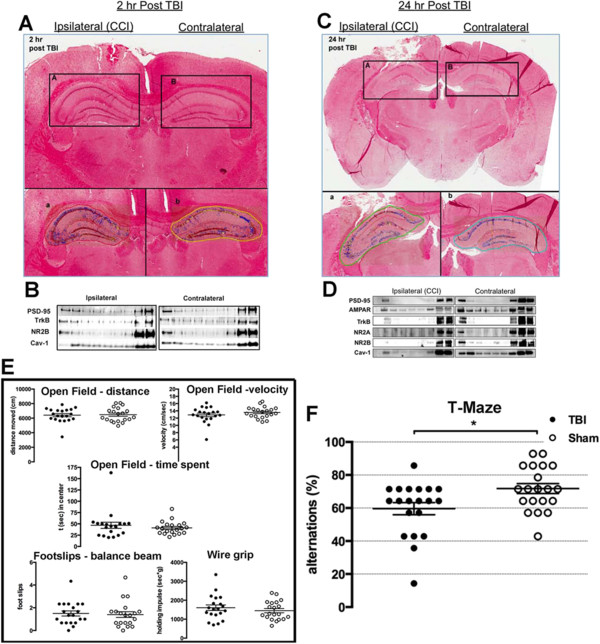
Controlled cortical impact (CCI) is a viable model of murine traumatic brain injury (TBI). (A) Trichrome stained paraffin section 2 hours post-CCI with both ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres. Bottom panels (a) and (b) are the enlargements of the hippocampal area outlined. (B) Sucrose density fractionation (SDF) to purify membrane/lipid rafts (MLRs) from ispilateral and contralateral hemispheres. Buoyant fractions contain the cholesterol and sphingolipid enriched MLR, while heavy fractions contain non-MLR cellular components. Western blot of SDF purification of MLR from ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres 2 hours post-CCI. (C) Trichrome stained paraffin section 24 hours post-CCI shows considerable damage to ipsilateral cortex and underlying hippocampus. Bottom panels (a) and (b) are the enlargements of the hippocampal area outlined. (D) Western blot of SDF purification of MLR from ipsilateral and contralateral hemispheres 24 hours post-CCI. (E) Behavior battery tests performed 3 months post-CCI: open field (distance, velocity, time spent), footslips and wire grip. (F) T-maze alternation behavioral test on sham and CCI groups after 3 months.
