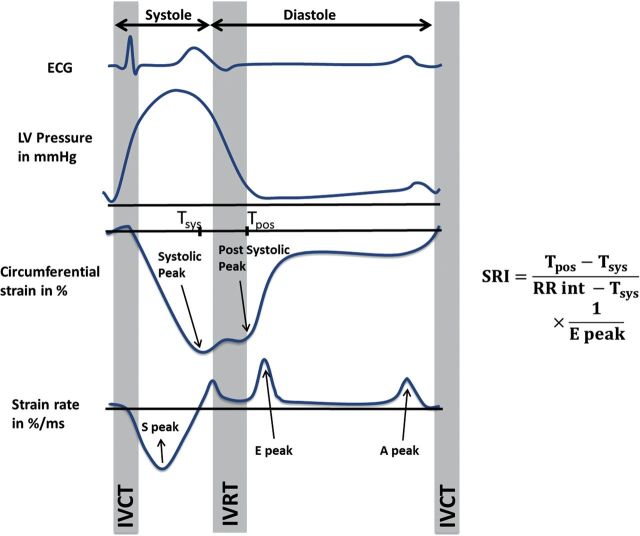
Figure 1.
This figure illustrating the calculation of the proposed SRI from the circumferential strain and strain rate curves. More negative strain values indicate greater circumferential shortening. SRI is calculated as the ratio of the duration of very early relaxation to that of the diastolic interval, divided by the early diastolic strain rate peak. The myocardial relaxation as imagined with a hypothetical pressure curve and electrocardiograph for reference. SRI: strain relaxation index; RR int: RR interval; S peak: peak systolic strain rate; IVCT: isovolumic contraction time; IVRT: isovolumic relaxation time; E peak: peak early diastolic strain rate; A peak: peak atrial-diastolic strain rate; Tsys: time of occurrence of peak systolic strain; Tpos: time of occurrence of post-systolic strain peak.