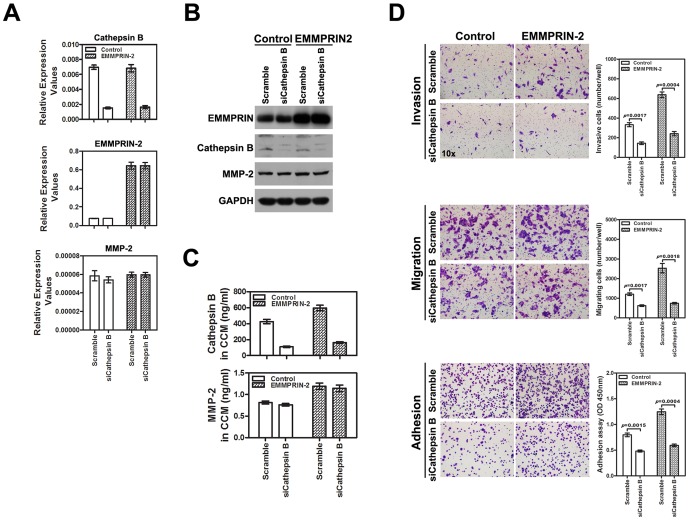
Figure 4. Cathepsin B is required for EMMPRIN-2-mediated invasion, migration and adhesion of head and neck cancer cells.
(A) Treatment with Cathepsin B siRNA resulted in corresponding reductions in Cathepsin B mRNA levels in both EMMPRIN-2 overexpressing and parental Tca8113 cells (p<0.05), while EMMPRIN-2 and MMP-2 were unaffected by Cathepsin B siRNA transfection (p>0.05). (B) The effects on Cathepsin B, EMMPRIN-2 and MMP-2 expression following Cathepsin B siRNA transfection in EMMPRIN-2 overexpressing and parental Tca8113 cells were further confirmed using western blot analyses. (C) The extracellular secretion of Cathepsin B was also reduced by siRNA treatment in Tca8113 cells both in the presence and absence of EMMPRIN-2 overexpression (p<0.05). (D) As observed in the experiments above, Tca8113 cells overexpressing EMMPRIN-2 displayed increased cell invasion, migration and adhesion as compared to parental Tca8113 cells. In contrast, down-regulation of Cathepsin B using siRNA significantly inhibited the invasion, migration and adhesion of Tca8113 cells overexpressing EMMPRIN-2.