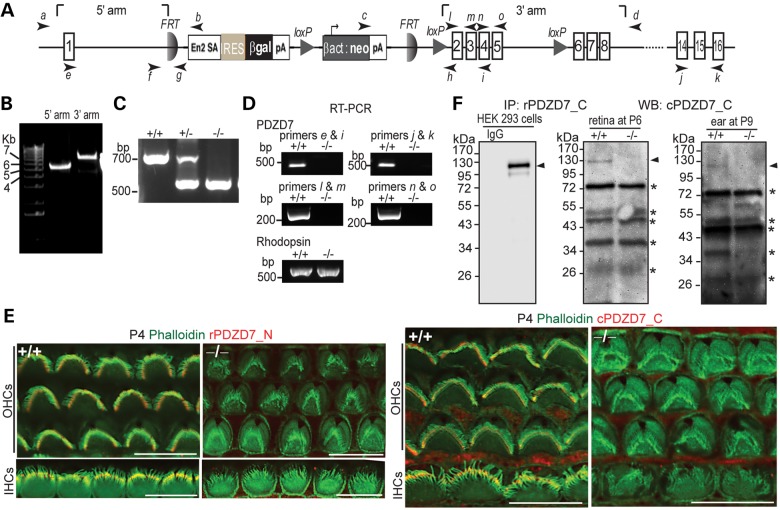
Figure 1.
Pdzd7−/− mice were generated. (A) A schematic diagram of the gene targeting Pdzd7tm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi allele. Arabic numerals in rectangles denote the exon numbers. Arrows with italic lower case letters label the position of primers used in this study. En2 SA, mouse engrailed 2 gene splice acceptor; IRES, internal ribosomal entry segment; βgal, β-galactosidase gene; pA, simian virus 40 polyadenylation signal; βact, human β-actin promoter; neo, neomycin phosphotransferase gene. (B) Confirmation of insertion of the targeting cassette into the Pdzd7 gene by PCR using primer pairs of a/b and c/d. (C) Identification of the mutant allele by routine genotyping PCR using primers, f, h and g. (D) Disrupted transcription of the Pdzd7 gene shown by RT–PCR analysis in the retina using primers e, i, j, k, l, m, n and o. RT–PCR of rhodopsin was used here as a positive control. Note: primer pairs of l/m, n/o and j/k were designed to amplify PDZ1, PDZ2 and PDZ3 regions of PDZD7 cDNA, respectively. (E) Immunofluorescence demonstrates loss of PDZD7 expression in Pdzd7−/− cochlear hair cells at P4. Scale bars, 10 µm. (F) Western blotting (WB) following immunoprecipitation (IP) found loss of PDZD7 expression in the retina at P6 (middle) and in the cochlea at P9 (right) in Pdzd7−/− mice. The same procedure was performed using PDZD7-transfected HEK293 cells (left). The band just above 34 kDa on the P9 inner ear blot showed no difference between wild-type and Pdzd7−/− littermates in another experiment at P5 (data not shown). Thus, it is considered non-specific. Arrowheads point to the PDZD7 bands. Asterisks mark non-specific bands. IgG, non-immune rabbit immunoglobulin; rPDZD7_C, rabbit antibody against PDZD7_C ; cPDZD7_C, chicken antibody against PDZD7_C; rPDZD7_N, rabbit antibody against PDZD7_N. +/+, wild-type; −/−, Pdzd7 knockout. The DNA sequences of primers are shown in Supplementary material, Table S1.