Figure 2. A role for DBP in tissue discrimination of 25OHD2 and 25OHD3.
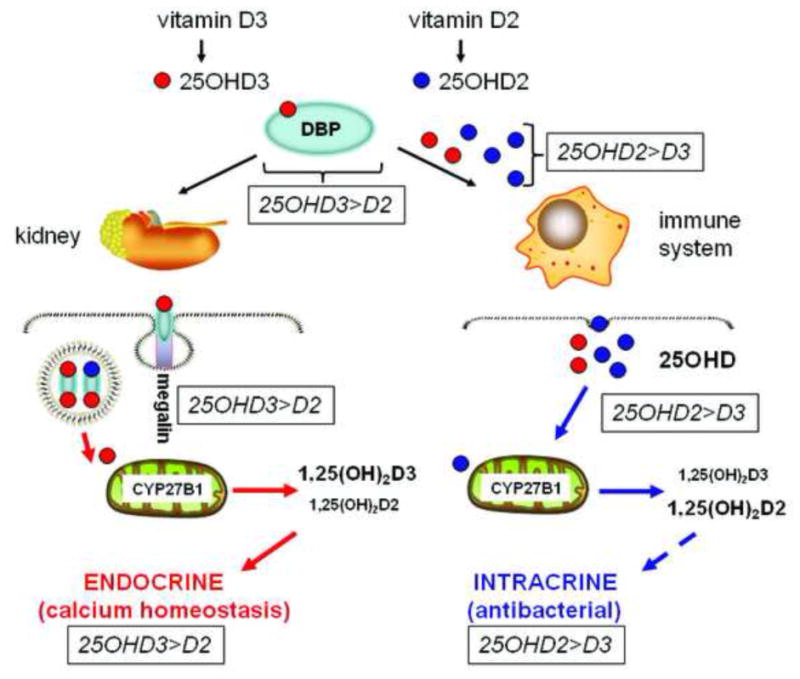
25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (25OHD2) binds to DBP with lower affinity than 25OHD3. This will impair renal handling of 25OHD2 relative to 25OHD3, providing a potential explanation for the relative inefficiency of supplementary vitamin D2 to achieve optimal serum levels of total 25OHD relative to supplementary vitamin D3. By contrast, for extra-renal tissues such as immune cells, impaired binding of 25OHD2 to DBP may facilitate enhanced bioavailability to target cells relative to 25OHD3. In this way, a lower total serum concentration of 25OHD2 may be as effective as a higher total serum concentration of 25OHD3 in promoting intracrine synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D and associated innate immune responses.
