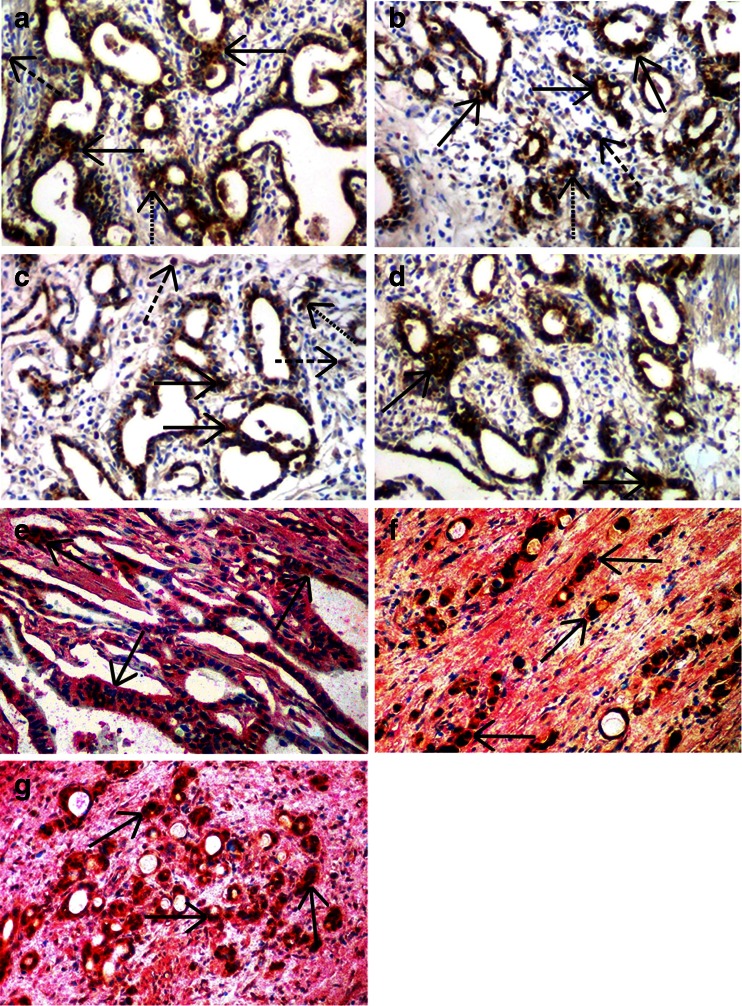
Fig. 1.
Specific staining (brown reaction product) by the immunohistochemical ABC peroxidase technique using polyclonal antibodies against coagulation factor X-FX (a), against protein Z-PZ (b) and against prothrombin fragment F1 + 2 (d), as well as a monoclonal antibody against protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor (ZPI) (c). Solid arrows indicate staining of tumor cell bodies in gastric cells, dotted arrows of endothelial cells, whereas dashed arrows of tumor-associated macrophages. Hematoxylin counterstain, original magnification ×100. Specific double staining Dako EnVisionTM technique (e, f, g) using polyclonal antibodies against FX and PZ as well as the monoclonal antibody directed to ZPI. e FX and ZPI (FX was visualized as dark brown reaction product, whereas PZ as red staining), f FX and PZ (factor X was visualized as red reaction product, whereas ZPI as dark brown staining), g PZ and ZPI (PZ was visualized as red staining, while ZPI as dark brown reaction product). The two colors are overlapping indicating co-expression of both proteins in gastric cancer cells (indicated by arrows). Hematoxylin counterstain, original magnification ×100