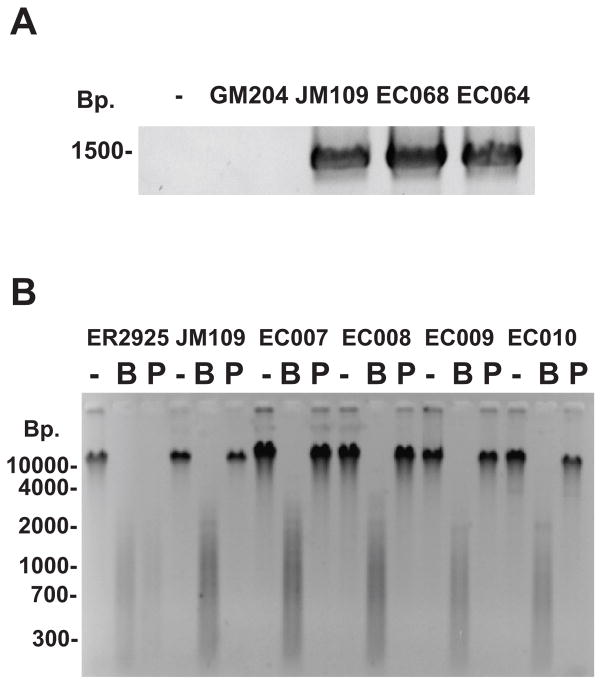
Figure 1.
A) Detection of the dcm gene via PCR. E. coli genomic DNA from different strains was used as a template for PCR using one forward dcm primer and two reverse dcm primers as described in the Materials and Methods. PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide straining. The negative sign (−) represents a no DNA control. E. coli GM204 DNA (GM204) contains deletion of the dcm operon. E. coli JM109 DNA (JM109) contains a wild-type dcm allele. EC068 and EC064 are DNAs from E. coli environmental isolates. B) Detection of 5-methylcytosine in 5′CCWGG3′ sequences using restriction enzyme isoschizomer pairs. DNA from E. coli ER2925 (dcm-6), JM109 (dcm+), and four environmental strains (EC007-EC010) were left undigested (−), digested with BstNI (B), or digested with PspGI (P). Reactions were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining.