Figure 19.
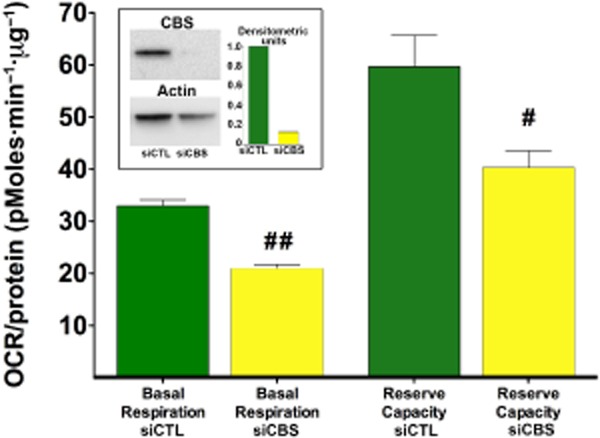
CBS silencing attenuates the bioenergetics in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans. The C. elegans wild-type N2 Bristol strain was obtained from the C. elegans Genetics Center, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA. Nematode culturing, synchronization and RNAi feeding were performed according to standard techniques (Vozdek et al., 2012). Egg isolation was done using the bleaching method. The resulting embryos were placed in S-complete medium without OP50 bacteria, and allowed to hatch overnight at 20°C with constant rotation. The L1 larvae were counted and supplemented with strain OP50 bacteria with pL4440-CBS or pL4440-scrambled RNAi feeding vector containing Ampicillin resistance marker to resume the life cycle. RNAi induction of bacteria was induced by IPTG. L1 larvae were transferred to a flask in a concentration of 80–100 worms·mL−1 in S-complete. To sterilize the animals, FUDR (5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine, Sigma-Aldrich) stock solution was added to each well 50 h after hatching. Five days after reaching adult stage, worms were washed with water and collected for subsequent Western blot analysis. For Western blot analysis followed by immuno-detection of CBS-1 a rabbit polyclonal antibody against recombinant CBS-1 was used. The general technique of the functional analysis of the metabolic activity of the worms was conducted using a 24-well Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analyzer as described (Houtkooper et al., 2013) with 50 worms per well under basal conditions and upon the addition of the uncoupling agent FCCP (10 μM). CBS silencing attenuated CBS-1 protein expression, and suppressed basal and FCCP-stimulated oxygen consumption. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of n = 20 determinations collected from three experimental days. Oxygen consumption was normalized to protein content. Statistical analysis was performed by anova followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test. #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 show lower oxygen consumption in the CBS-1 silenced group, when compared to the respective sham-silenced controls.
