Figure 2).
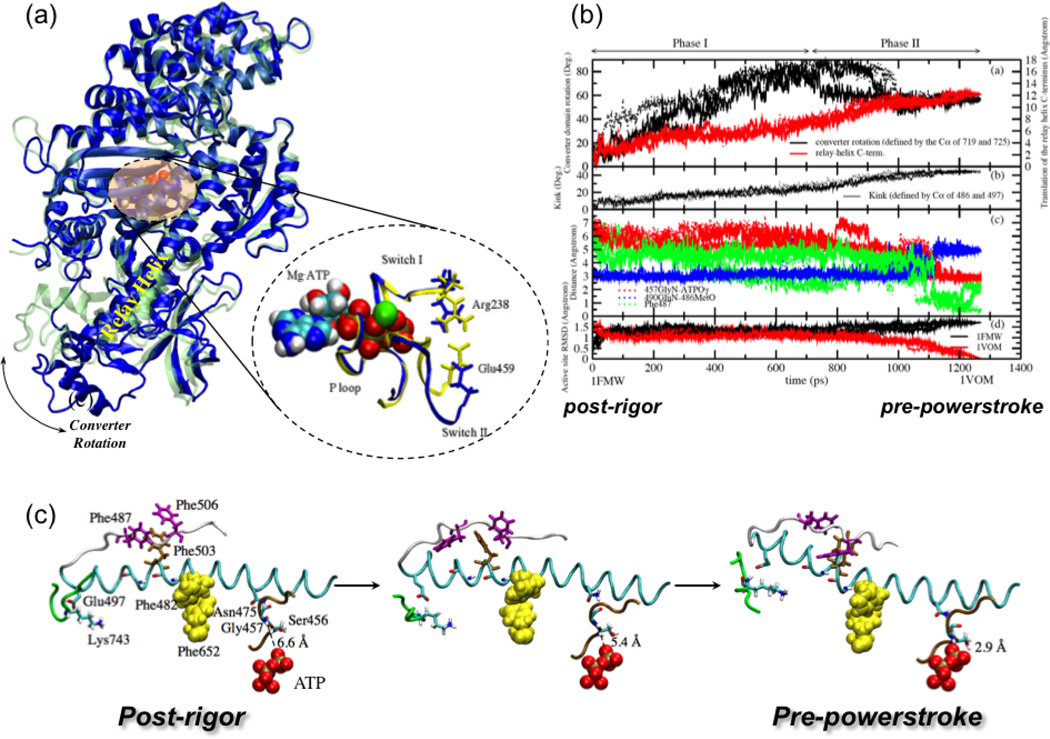
The recovery stroke of myosin II, which is the conversion between the post-rigor and pre-powerstroke kinetic states. (a) Structural differences between two X-ray conformations (post-rigor71, in blue, and pre-powerstroke72, in green) of the Dictyostelium discoideum myosin motor domain. The most visible transition is the converter rotation, although there are also notable changes in the nucleotide binding site and the relay helix that connects the converter and the nucleotide binding site. With bound, the nucleotide binding site of the pre-powerstroke state has a closed configuration (in yellow); with ATP bound, the nucleotide binding site in the post-rigor state is open (in blue) due to displacement of the Switch II loop.(b) Variation of critical structural parameters along the three Targeted Molecular Dynamics (TMD) trajectories for illustrating the sequence of events along the approximation transition paths for the recovery stroke40. (c) Three snapshots (at 0.0 ps, 630.0 ps, 1270.0 ps) from one of the three TMD simulations, in the same format as Fig.2 in Ref.68 for comparison, to illustrate the proposed coupling between the small motion of SwII with the large translation of the relay helix C-terminus.