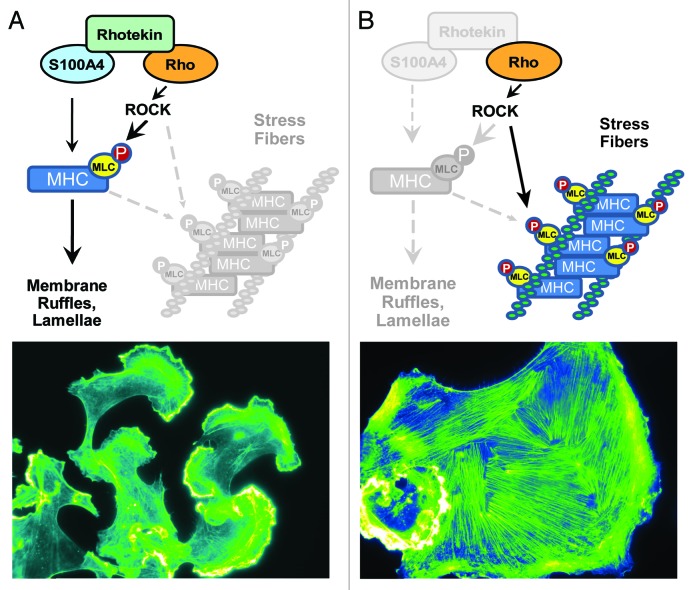
Figure 3. Mechanisms of S100A4-Rhotekin-RhoA crosstalk in mediating membrane ruffling. (A) We propose that S100A4-mediated inhibition of myosin IIA heavy chain oligomerization limits the contractility of pMLC-myosin IIA complex. Under this condition, the actin polymerization functions of ROCK (shown here) and other effectors such as mDia (not shown) predominate, thus permitting the formation of lamellae. The lower panel depicts MDA-MB-231 cells stimulated with EGF for 5 min and then stained with phalloidin. (B) In the absence of S100A4 and Rhotekin, Rho/ROCK-mediated MLC phosphorylation in the presence of oligomers of myosin IIA facilitates the contractility required for stress fiber formation, while preventing membrane ruffles downstream of RhoA from forming. The lower panel represents an extreme phenotype of MDA-MB-231 cells with RNAi-mediated reduction of S100A4 and Rhotekin that were stimulated with EGF for 5 min and then stained with phalloidin.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.