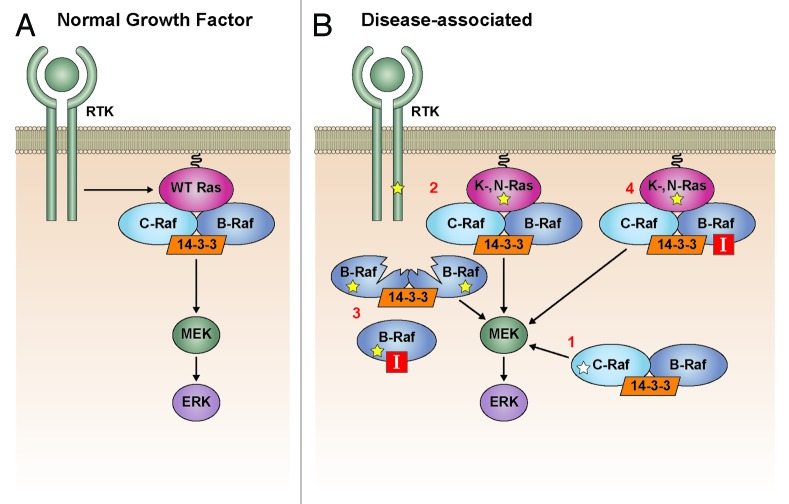
Figure 3. Raf dimerization in cell signaling. (A) In normal Ras-dependent growth factor signaling, Raf dimerization is required for Raf kinase activation and signaling to MEK (left). (B) In disease-associated states, Raf dimerization is required for upregulated MEK/ERK signaling induced by (1) disease-associated mutant Raf proteins with intermediate and impaired kinase activity, (2) mutationally-activated receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) and RasGTPases, (3) self-homodimerizing V600E-B-Raf splice variants that mediate Raf inhibitor resistance, and (4) treatment with ATP-competitive Raf inhibitors in the presence of activated Ras. Yellow stars indicate oncogenic mutations and white star indicates a Rasopathy mutation.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.