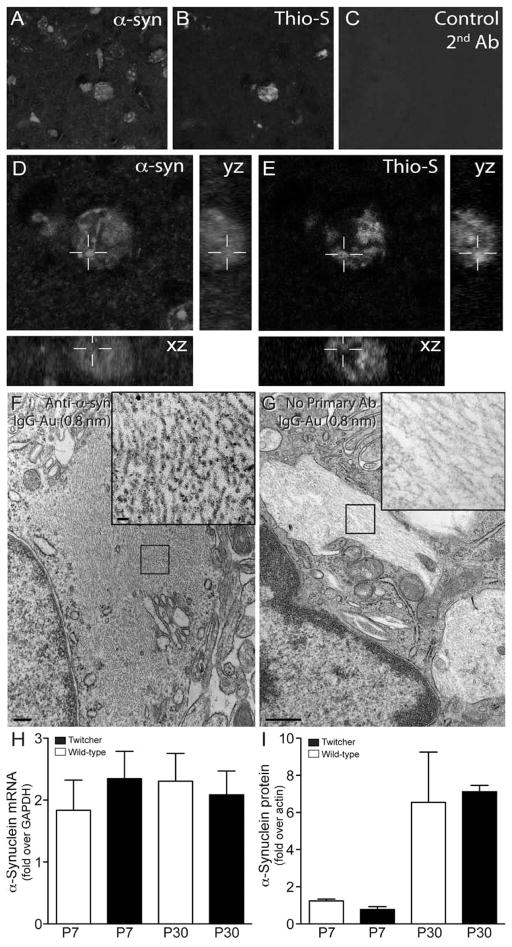
Figure 4. Thioflavin-S reactive inclusions contain α-synuclein.
A–E) Sections of P30 Twitcher brain were doubly stained with a monoclonal antibody to α-synuclein (A, D) and thioflavin-S (B, D). Sections were scanned using confocal microscopy and orthogonal yz, xz reconstructions rendered using ImageJ software (NIH). α-synuclein was detected to be predominantly associated with thioflavin-S reactive inclusions. F, G) Free floating sections of mutant caudate were immunostained for α-synuclein and processed for immunoelectron microscopy using secondary antibodies conjugated with 0.8 nm gold particles. Inclusions in mutant neurons (F, inset) showed positive immunoreaction. Control of non-specific binding using secondary-Au antibodies showed no reaction (G, inset). H, I) Analyses for mRNA (H) and protein (I) levels of α-synuclein were done by RT-PCR and immunoblotting using P7 and P30 Twitcher and WT brain. Immunoblotting was performed with antibodies recognizing actin and monomeric forms α-synuclein. Detectable bands representing α-synuclein where quantified as the fold increase over actin using ImageJ software (NIH). Levels of α-synuclein mRNA and protein were not significantly different between Twitcher and WT at either time point.