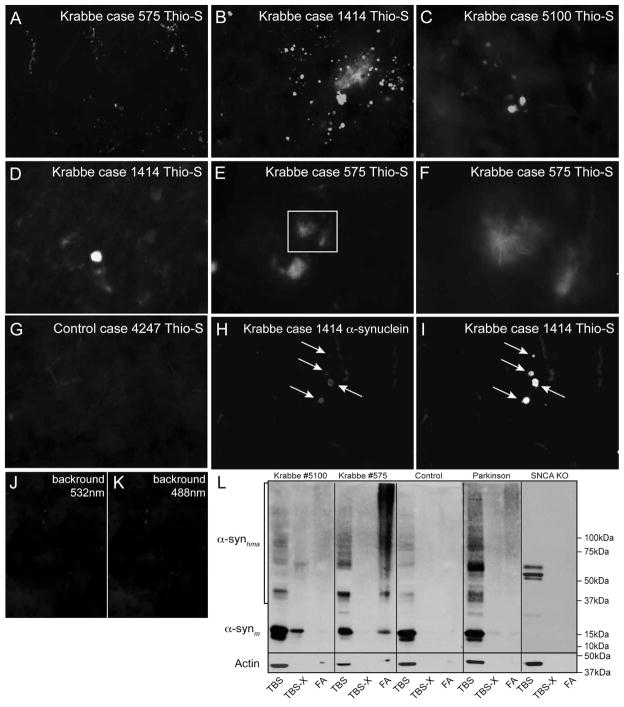
Figure 5. Thioflavin-S reactive inclusions of aggregated α-synuclein are present in the brain of Krabbe human patients.
A–G) Autopsied frontal cortex samples from three human cases of infantile Krabbe disease were obtained and processed for thioflavin-S staining. All three cases of infantile Krabbe disease were affected by abundant thioflavin-S reactive deposits, which were primarily located in the cortical grey matter. Most inclusions appeared as an amorphous material (D) but others showed a core of dense thioflavin-S positive material decorated with filamentous fibrils irradiating from the core center (inset in E magnified in F). Sections from age-matching control human brains were devoid of thioflavin-S reactive material (G). H–K) Double immunohistochemistry detected the presence of aggregated α-synuclein (I) in most thioflavin-S inclusions (H). Images in J, K are controls of background fluorescence and show non-specific fluorescence originating from blood cells in brain vessels. Images in A–C and G–K were collected using a 40× objective. Images in D–F were collected using a 63× objective. L) SDS-PAGE separations of TBS, TBS-triton-X (TBS-X) and formic acid (FA) protein extracts from age-matching control and infantile Krabbe basal ganglia were immunoblotted with monoclonal antibodies against epitopes in monomeric α-synuclein. Monomeric α-synuclein (~15kDa) was present only in the TBS and some TBS-X fractions. An increased amount of high molecular weight aggregates of α-synuclein (α-synhma) were visible in the Krabbe samples for all fractions. A sample of frontal cortex from a Parkinson’s disease case was included as a positive control showing levels of high molecular weight α-synuclein similar to the amount seen in Krabbe tissue. Whole cell brain lysate from a one month-old SNCA KO mouse was also included which showed no detectable monomeric α-synuclein and only a few additional non-specific bands.