Fig. 1.
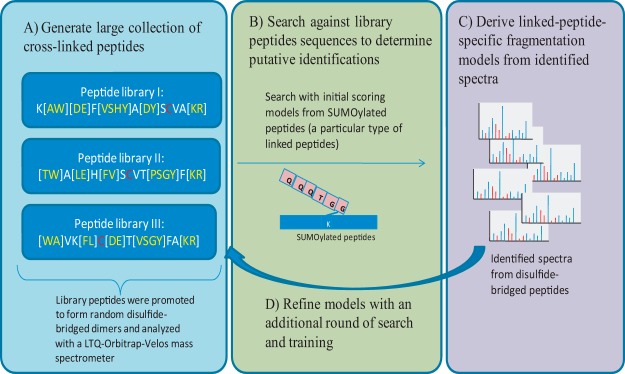
Generating training data using combinatorial synthetic peptide libraries. A, in order to generate a sufficiently large training dataset for linked peptides, we designed and synthesized three combinatorial peptide libraries, each with a cysteine residue at a different position along the peptide sequence. Amino acids in square brackets indicate that multiple residues are possible at that position. The peptide libraries were allowed to form disulfide-bridged dimers and were analyzed using an LTQ-Orbitrap-Velos mass spectrometer. MS/MS spectra from the disulfide-bridged peptide libraries were identified using a two-step strategy. B, an initial set of MS/MS spectra from disulfide-bridged peptides was identified using scoring models learned from SUMOylated peptides (a special type of linked peptide in which the C termini of QQQTGG is linked to the lysine of another peptide). C, from these initial training data, we built a scoring model specific for disulfide-bridged peptides and (D) used the improved scoring models to search the data again to obtain a final set of spectra from disulfide-bridged peptides.
