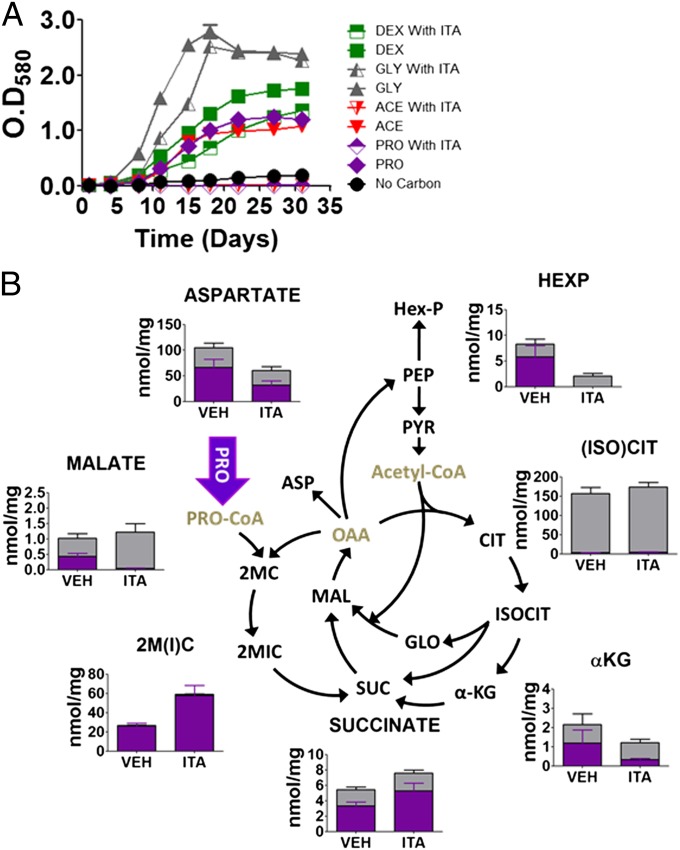
Fig. 4.
Chemical-phenotypic characterization of the ICL-specific inhibitor, itaconic acid, on intact wild-type Mtb. (A) Growth phenotypes of wild-type Mtb H37Rv in the presence and absence of 2 mM itaconic acid when cultured in m7H9 media containing 0.2% carbon sources as indicated. ACE, acetate; DEX, dextrose; GLY, glycerol; ITA, itaconic acid; PRO, propionate. (B) Intrabacterial pool sizes and isotopic labeling of select intermediates of Mtb central carbon metabolic pathway when cultured in media containing [U-13C]propionate for 24 h. Total bar heights indicate the intrabacterial concentration, whereas purple colored area of each bar denotes the extent of 13C labeling achieved following transfer to [U-13C] carbon source. αKG, α-ketoglutarate; 2MC, 2 methylcitrate; 2M-ACO, 2 methyl cis-aconitate; 2MIC, 2 methylisocitrate; Asp, aspartate; cis-ACN, cis-aconitate; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; FUM, fumarate; GLO, glyoxylate; Hex-P, hexose phosphate; IC, ion counts; MAL, malate; Pent-P, pentose 5-phosphate; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PYR, pyruvate; SH7P, sedoheptulose 7-phosphate; Triose-P, triose 3-phosphate (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate). All values are average of three independent experiments, each of which consisted in biological triplicates, ± SE.