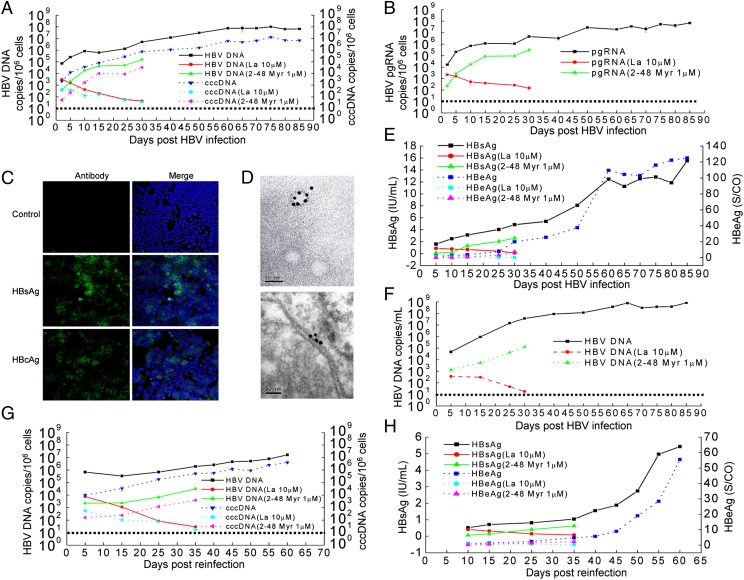
Fig. 2.
Infection of HLCZ01 cells by HBV. (A) Kinetics of intracellular viral DNA and cccDNA in HLCZ01 cells inoculated with the supernatant of HepG2.2.15 cells. The supernatant from HepG2.2.15 cells was mixed with the HBV large-surface, protein-derived peptide (amino acids 2–48). Then HLCZ01 cells were inoculated with the mixture at an MOI of 20 Geq per cell. Alternately, HLCZ01 cells were inoculated with the supernatant of HepG2.2.15 cells at an MOI of 20 Geq per cell and were cultured in the presence of 10 μM lamivudine. Intracellular HBV DNA or cccDNA measured by real-time PCR is shown as the number of HBV DNA or cccDNA copies per 106 cells. (B) The kinetics of viral pregenomic RNA within HLCZ01 cells inoculated with the supernatant from HepG2.2.15 cells. HLCZ01 cells were treated as described in A. The viral pregenomic RNA level determined by real-time PCR is shown as the number of HBV pregenomic RNA copies per 106 cells. (C) Immunofluorescence of HBsAg or HBcAg in HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells. HLCZ01 cells were inoculated with the supernatant of HepG2.2.15 cells. Cells were harvested for immunostaining at 40 dpi using mouse monoclonal anti-HBsAg or anti-HBcAg antibody. DAPI was used for nuclei counterstaining. Identical settings were maintained for image capture. (D) Immunoelectron micrographs of HBsAg-positive particles in the supernatant and the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum of HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells. HLCZ01 cells were treated as described in C. The supernatants (Upper) or cells (Lower) were immunostained for observation under electron microscopy. Dense, dark particles are HBsAg-positive particles. (Scale bar, 50 nm.) (E) ELISA for HBV-specific proteins. HLCZ01 cells were treated as described in A. HBsAg and HBeAg in the supernatant of HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells were detected by ELISA. (F) Kinetics of HBV DNA in the supernatant of HLCZ01 inoculated with the supernatant of HepG2.2.15 cells. HLCZ01 cells were treated as described in A. The viral DNA in the supernatant as determined by real-time PCR is shown as the number of HBV copies per milliliter of supernatant. (G) Detection of viral DNA and cccDNA in HLCZ01 cells inoculated with the supernatant of HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells. HLCZ01 cells were inoculated with the supernatant of HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells in the presence of the HBV large-surface, protein-derived peptide or lamivudine. The viral DNA or cccDNA replication was measured by real-time PCR. (H) ELISA for HBV-specific proteins. HLCZ01 cells were treated as described in G. HBsAg and HBeAg in the supernatant were detected by ELISA. Horizontal dashed lines indicate the low limit of quantification (LLOQ) of the assay.