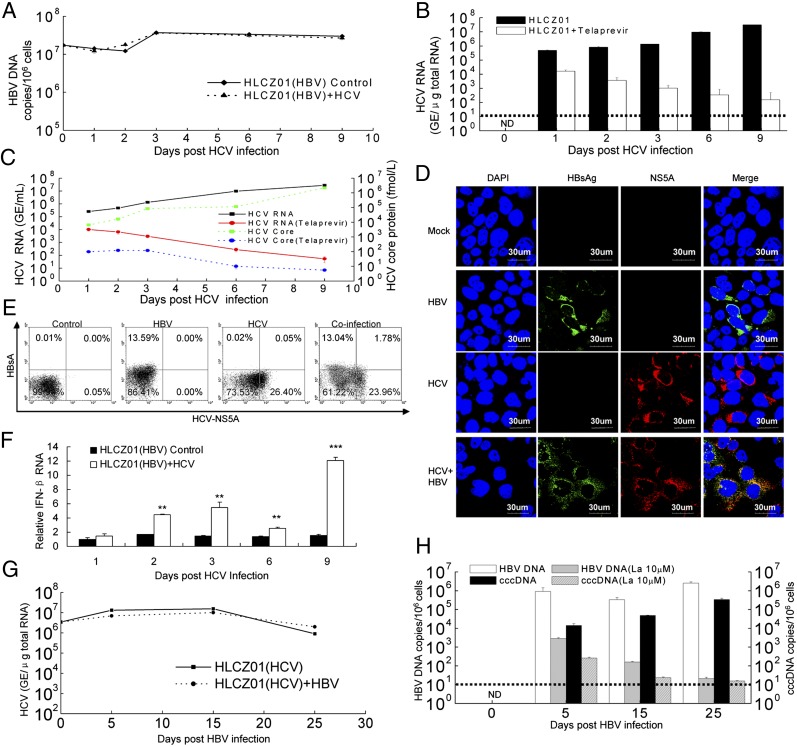
Fig. 6.
HBV/HCV coinfection in HLCZ01 cells. (A and B) HCV infection has no effect on HBV replication. HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells were infected with JFH1 viruses in the presence of 5 µM telaprevir. Intracellular HBV DNA (A) and HCV RNA (B) were measured by real-time PCR. (C) Detection of HCV RNA and core protein in the supernatant of HCV-infected HLCZ01 preinfected with HBV. HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells were treated as in A. HCV RNA and core protein in the supernatant were examined by real-time PCR and ELISA, respectively. (D and E) Infection of HLCZ01 cells by both viruses. HLCZ01 cells were infected with HBV for 10 d. Then HBV-infected cells were infected with HCV for another 6 d. (D) Cells were fixed for immunostaining using monoclonal anti-HCV NS5A (red) and anti-HBsAg (green) antibodies. DAPI (blue) was used to counterstain nuclei. Identical settings were maintained for image capture. Representative images are shown. (E) Frequency of HLCZ01 cells that are coinfected with both HBV and HCV as determined by flow cytometry. Cells were collected for flow cytometry using anti-HBsAg and anti-HCV NS5A antibodies. The data are from one experiment that is representative of three independent experiments. (F) HBV has little effect on the innate immune response of HLCZ01 cells to HCV infection. HBV-infected HLCZ01 cells were infected with JFH1 virus. IFN-β mRNA was examined by real-time PCR and normalized with GAPDH. The results are the average of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. (G and H) HBV infection does not affect HCV replication in HLCZ01 cells. HCV-infected HLCZ01 cells were infected with HBV in the presence of 10 µM lamivudine. Intracellular HCV RNA was verified by real-time PCR (G). HBV DNA and cccDNA in the cells were examined by real-time PCR (H). ND, not detectable. Horizontal dashed lines indicate the LLOQ of the assay. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus control.