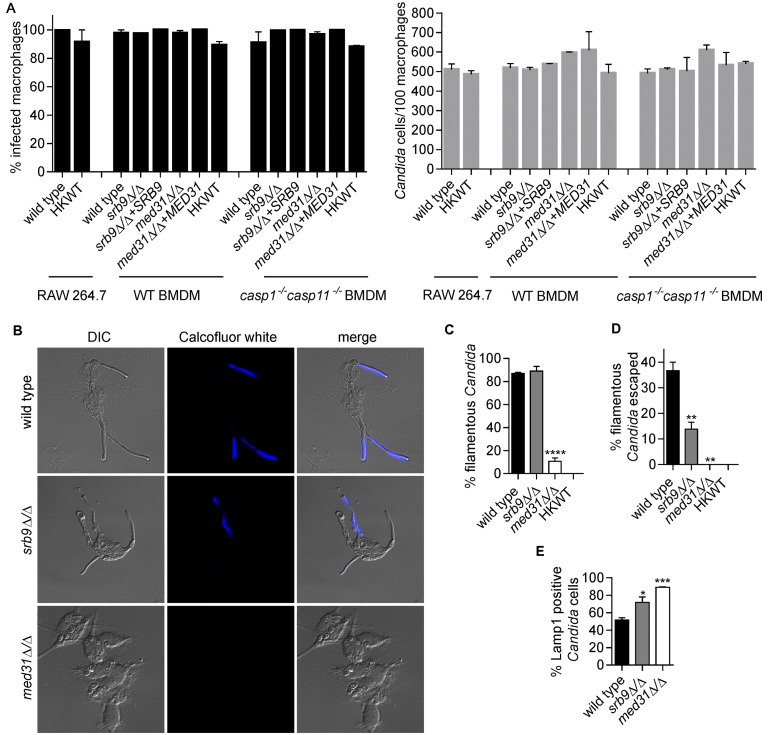
FIG 2 .
Mediator regulates morphogenesis and escape of C. albicans from macrophages. (A) Percentages of infected macrophages and numbers of Candida cells/100 macrophages were determined from images from the live-cell microscopy experiments represented in Fig. 1B and 3. Three independent biological experiments were performed for BMDMs and two for the RAW 264.7 cell line, and a total of 200 macrophages were counted in each of the experiments. Values are means ± SEM. HKWT, heat-killed wild-type cells. (B and C) Wild-type C. albicans and med31∆/∆ and srb9∆/∆ strains were used to infect wild-type BMDMs, and fungal cell morphology was assessed by microscopy and quantified at 3 h postphagocytosis by counting at least 200 cells/strain. Averages and SEM of the results of 3 independent experiments are shown. ****, P ≤ 0.0001. DIC, differential interference contrast. (D) Percentages of escaped C. albicans hyphae and calcofluor white (CW)-stained hyphae were determined by counting total cells in macrophages from bright-field images (see images in panel B). CW stains only fungal cells that are outside the macrophages, while the phagocytosed cells are protected. At least 200 cells/strain were counted. Data represent averages and SEM (n = 3). **, P ≤ 0.01. (E) Association of C. albicans with late phagosomes in wild-type BMDMs was monitored by immunofluorescence by staining for the phagosomal marker Lamp1. Lamp1-positive C. albicans cells were scored by microscopy (images are shown in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material) at the 2-h time point (following the 1-h coincubation). Three independent experiments were performed, and at least 50 Candida cells were counted in each. Averages and SEM are shown. *, P <0.05; ***, P <0.001.