Figure 1.
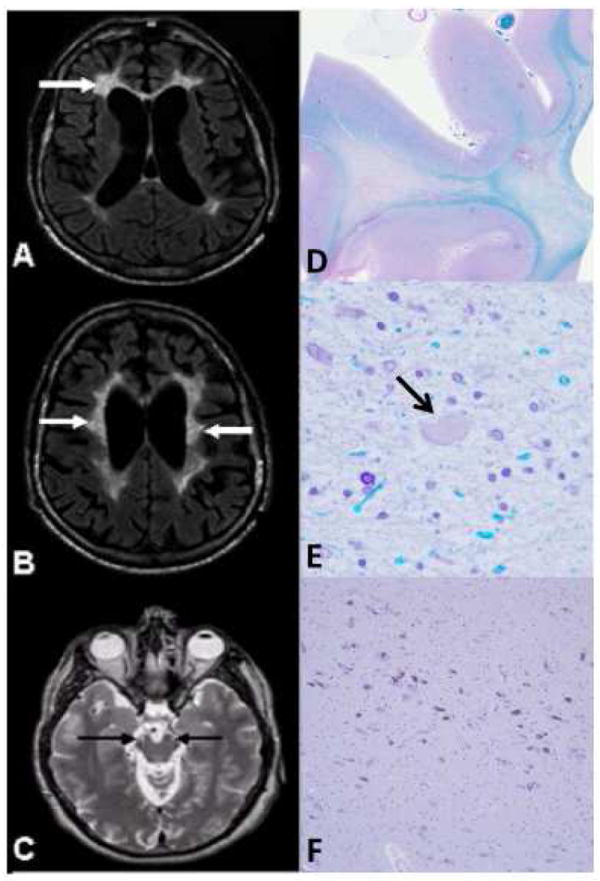
MRI (A-C) and neuropathology (D-F) of HDLS cases with CSF1R mutations
A, B) Axial FLAIR MRI images; C) Axial T2-weighted MRI image. A) Localized, periventricular, deep, and subcortical white matter lesions (WML), more severe on the left side (arrows). B) Bilateral frontoparietal WML involving periventricular, deep, and subcortical areas with U-fiber sparing (arrows). C) Involvement of the corticospinal tracts bilaterally (arrows) at the level of the mesencephalon. D, E) Luxol fast blue; F) Hematoxylin-eosin. D) Myelin loss in the white matter of the superior frontal lobe. E) Tissue vacuolation with axonal spheroids (arrow) (magnification: ×400). F) The ventrolateral part of substantia nigra has minimal focal neuronal loss with extraneuronal neuromelanin (magnification: ×100).
