Figure 1.
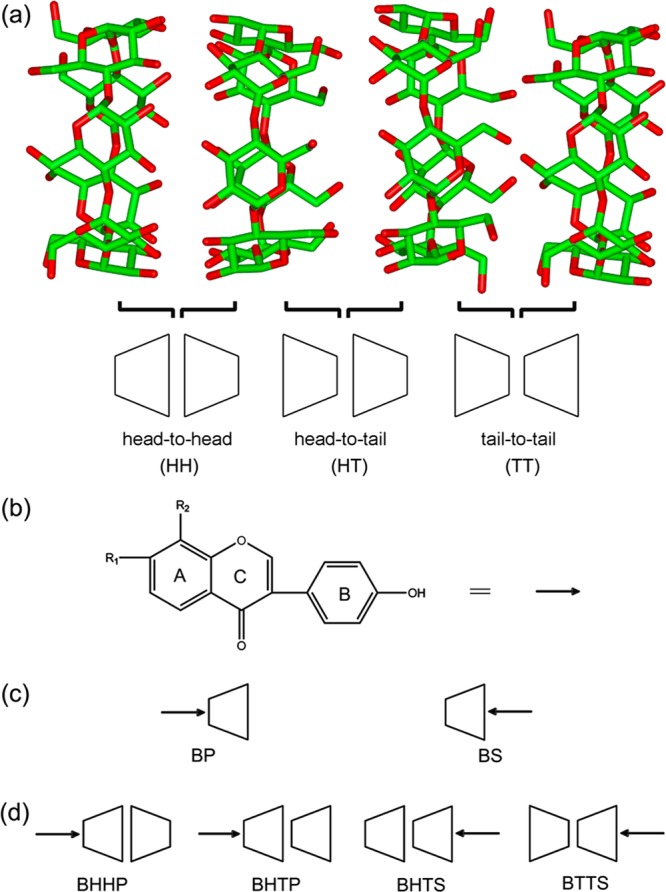
Molecular structure of (a) β-CD dimers and (b) isoflavone guests and possible [host:guest] binding modes with stoichiometric ratios of (c) 1:1 and (d) 2:1. Head means the secondary rim of β-CD and tail the primary rim. The guest molecules include puerarin (R1 = H, R2 = glucose), daidzin (R1 = glucose, R2 = H), and daidzein (R1 = H, R2 = H). A, B, and C denote relevant isoflavone rings. The arrow indicates the guest molecule and the orientation that the guest penetrates into β-CD cavity.
