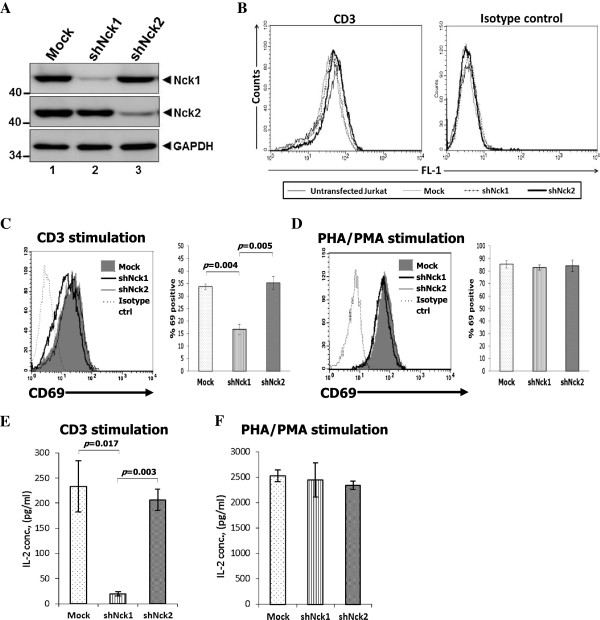
Figure 1.
Nck1 is required for TCR-mediated CD69 expression and interleukin (IL)-2 production. A) Jurkat T cells were transfected with a control vector, Nck1- or Nck2-specific shRNA expression vector. Transfected cells were selected in medium containing 4 μg/ml puromycin for 4–7 days before cloning by limiting dilution. Cell extracts were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-Nck1, −Nck2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) and anti-GAPDH mAb. B) The expression levels of surface CD3 molecules of the cloned cells from each population were measured by flow cytometry. C-D). Nck1-knockdown (shNck1), Nck2-knockdown (shNck2) and control cells (mock) were stimulated with 1 μg/ml anti-CD3 antibody-coated plates (C) or 6 μg/ml PHA plus 1 ng/ml PMA (D) for 24 h. Each cell population was stained with anti-CD69 conjugated phycoerythrin (PE) and isotype control antibody and then analysed by flow cytometry. The expression of CD69 was displayed in both histogram (left) and bar graph (right). For bar graph, the fraction of cells expressing CD69 in each population was normalized to its isotype control. E-F) Cells were stimulated as in C-D. The supernatants from CD3 (E) and PHA/PMA stimulation (F) were measured for IL-2 production by ELISA. Results from CD69 expression and IL-2 production are shown as mean ± SD from triplicate samples and were compared among the groups by using the two-tailed unpaired t test. The p-value less than 0.05 were considered for statistical significance. Data are representative of three independent experiments.