Fig. 2. Apelin is required for zebrafish lymphatic vessel formation.
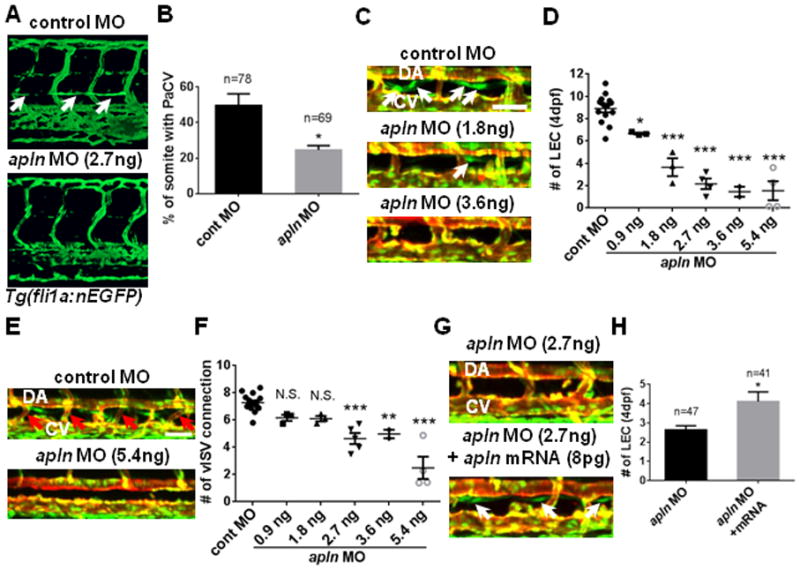
(A) The loss of parachordal vessel (white arrows) in 3dpf apln MO-injected embryos in Tg(fli1a:nEGFP) transgenic background. (B) Quantification of the formation of parachordal vessel (PaCV) at 3dpf. (C) Representative images of 4dpf apln MO-injected embryos in the trunk region. White arrows point to LECs within the thoracic duct. The deficit in the number of LECs progressively worsened as the dose of apln MO increases. (D) Quantification of the number of LECs in control and apln MO-injected embryos at 4dpf. LECs located between 8th and 15th somites were counted. Each dot represents an individual set of experiments. Total number of embryos are; control MO=96, apln MO 0.9ng=26, 1.8ng=30, 2.7ng=37, 3.6ng=19, and 5.4ng=29. (E) The loss of venous ISVs (red arrows; vISV) in 4dpf embryos injected with a high dose of apln MO. (F) Quantification of the number of vISVs in control and apln MO-injected embryos. Each dot represents an individual set of experiments. Total number of embryos are; cont MO=103, apln MO 0.9ng=26, 1.8ng=30, 2.7ng=48, 3.6ng=19, and 5.4ng=27. (G) Over-expression of synthetic apln mRNA can rescue lymphatic defects in apln MO-injected embryos. White arrows point to LECs in embryos co-injected with synthetic apln mRNA and apln MO. (H) Quantification of the number of LECs at 4dpf in embryos injected with apln MO alone and in embryos co-injected with apln MO and synthetic apln mRNA. DA, dorsal aorta; CV, cardinal vein. Scale bars are 50μm.
