Fig. 5. Apelin and Vegfc signaling are not redundant but functionally synergize to facilitate lymphatic development in zebrafish.
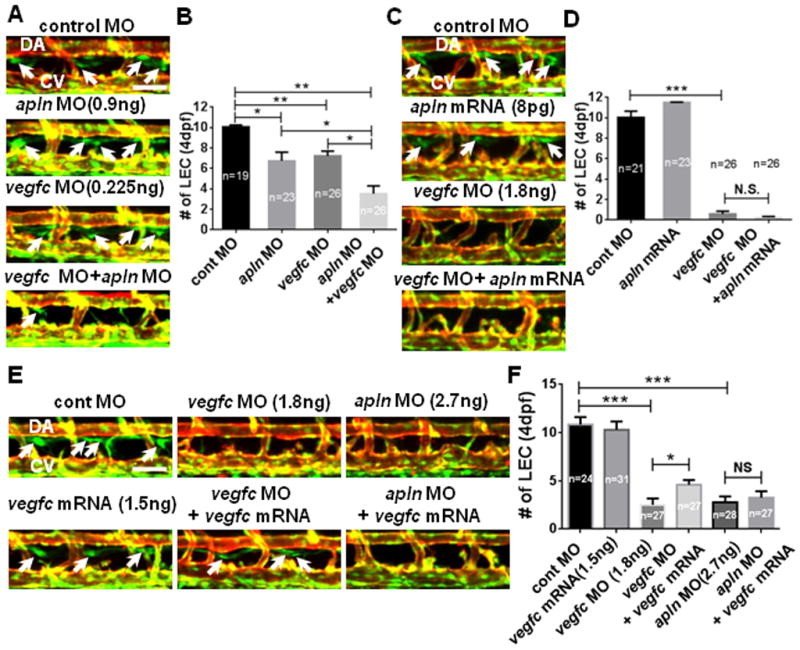
(A) Apelin and Vegfc signaling may synergistically promote lymphatic development. 4dpf embryos co-injected with low doses of apln and vegfc MOs contained a substantially decreased number of LECs (arrows) compared to control or single MO injected embryos. (B) Quantification of the number of LECs. (C) Apelin signaling may have a non-redundant role with Vegfc signaling during LEC development. Over-expression of Apelin by mRNA injection did not alleviate lymphatic defects in 4dpf vegfc MO-injected embryos. (D) Quantification of the number of LECs. (E) Representative images for the lymphatic vessel phenotype in 4dpf Tg(fli1a:nEGFP);Tg(kdrl:mCherry) embryos injected with apln and vegfc MOs and vegfc mRNA. vegfc mRNA injection at 1–2 cell stage only rescues the defects caused by Vegfc knockdown, but not Apln knock-down. (F) Quantification of LECs. DA, dorsal aorta; CV, cardinal vein. Scale bars are 50μm.
