Fig. 2.
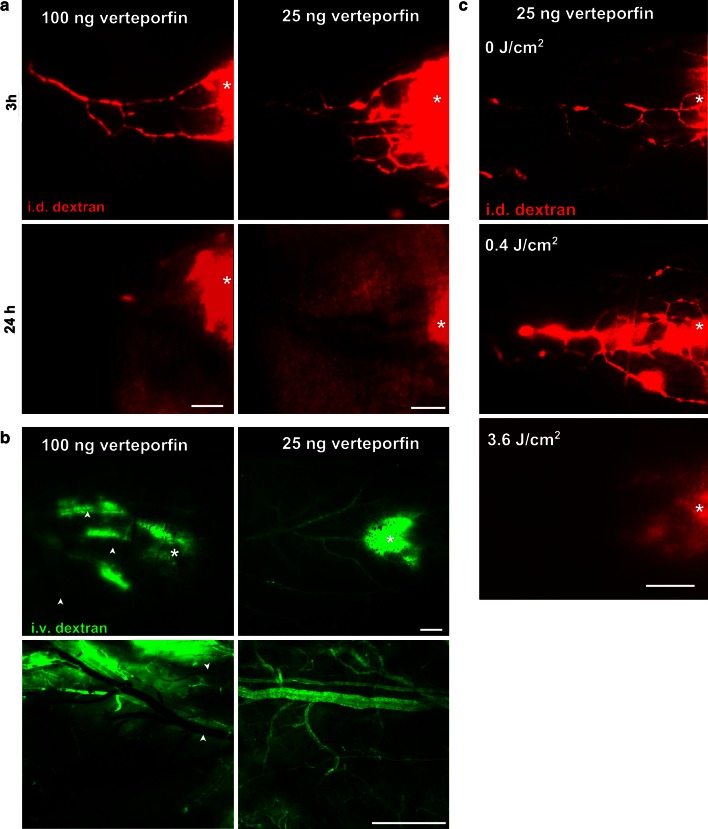
Lymphatic-specific targeting by PDT can be achieved with low doses of intradermally injected photosensitizer. a Fluorescence microlymphangiography 3 and 24 h post-PDT shows blockage of lymphatic drainage with both 100 ng (left) or 25 ng (right) of verteporfin. b Fluorescence angiography 24 h after PDT. Blood vessel integrity as revealed by intravascular injection of FITC-dextran (green) 24 h post-PDT shows vascular blockage with 100 ng verteporfin (left) in all 7 ears tested but no apparent vascular blockage with 25 ng verteporfin (right) in 6 out of 7 tested ears (p = 0.0047, Fisher exact test). In any case, dextran leaked from blood vessel at the sites of verteporfin injection (star). Top panel fluorescence angiography in dorsal ear skin imaged through the intact ear. Bottom panel high resolution fluorescence angiography in dorsal ear after surgical resection of ventral skin and cartilage. c Lymphatic drainage function 24 h after PDT (with 25 ng verteporfin) by fluorescence microlymphangiography with TRITC-dextran (red) shows that a light fluence of 3.6 J/cm2 but not 0.4 J/cm2 could occlude lymphatic drainage in the ear. Bar 500 μm