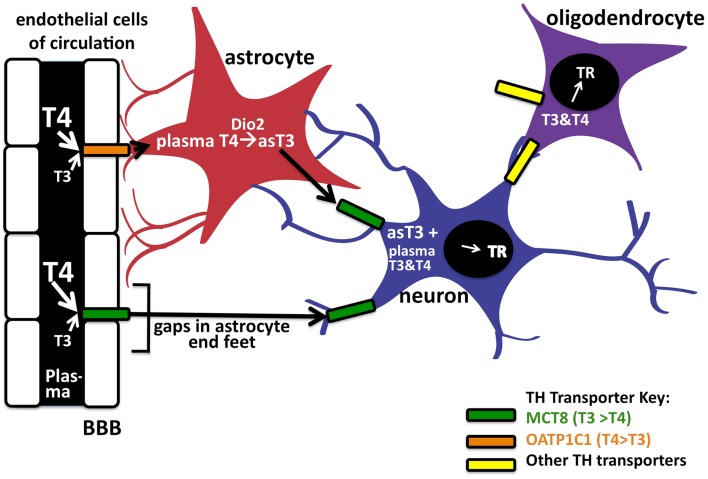
Figure 2.
Entry of TH into brain via the blood–brain barrier. TH can enter neurons by two pathways. The first is by crossing the endothelial cells of the blood–brain barrier (BBB) by the OAT1P1C transporter to enter astrocyte end feet (in red). After entering astrocytes, T4 can be converted into T3 via deiodinase 2, to enter the neuron (in blue) by the MCT8 transporter. Circulating T4 and T3 may also enter neurons (and astrocytes) directly via these transporters through gaps in the astrocyte end feet. Oligodendrocytes (purple), which express TRs, are also known TH cell targets in the CNS. There is also evidence of as-yet unknown TH transporters in the brain; the TH transporters, and their known preferences for T4 or T3, are indicated in color codes on the right.