FIGURE 1.
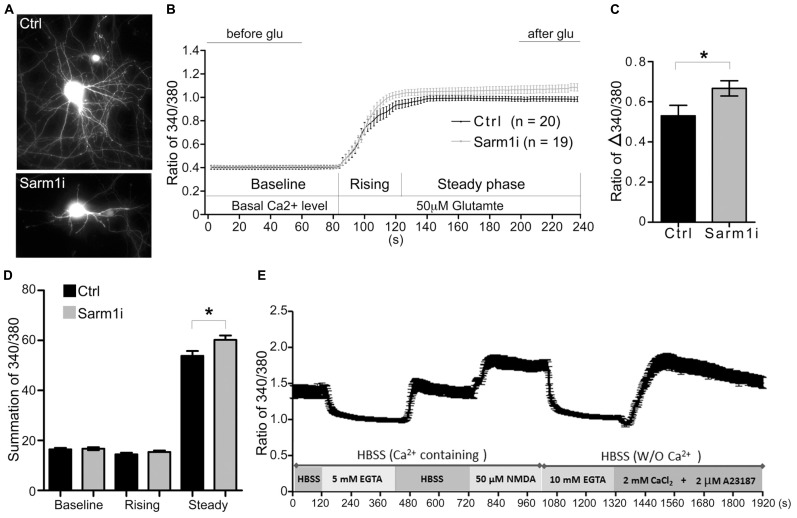
Sarm1 knockdown enhances Ca2+ influx after glutamate treatment in cultured hippocampal neurons. (A) Representative images of hippocampal neurons that have been transfected with a control vector (Ctrl) or a Sarm1 shRNA expressing construct (Sarm1i). (B) Calcium imaging after glutamate stimulation is shown. The Ca2+ signal in the soma was monitored by Fura-2 for basal Ca2+ levels between 0 and 90 s. After glutamate perfusion, a strong Ca2+ influx response was induced, as shown by the dramatic increase in the 340/380 ratio. The entire response was separated into three phases (baseline, rising, and steady), as indicated. (C) The ratio of Δ340/380 is shown. The means of the last 40 s (after glu) and the first 60 s (before glu) in (B) were calculated to determine the ratio of Δ340/380 upon glutamate stimulation. (D) The summations of the 340/380 ratio of the baseline, rising and steady phases shown in (B). (E) WT neurons were subjected to a series of treatments, as indicated. After NMDA treatment, the calcium concentration was able to return to the baseline and respond to calcium ionophore A23187 to cause calcium influx. The values represent the means ± SEMs. The sample sizes (n) are indicated. *P < 0.05.